Do you suspect a loved one might be using drugs, but you’re unsure of the signs? Recognizing the high on drugs symptoms is critical for identifying addiction and intervening before it’s too late. Drug use has wide-ranging effects, from physical and behavioral changes to substance-specific symptoms.
Early detection is key for successful rehabilitation as risk factors include genetic predisposition and environmental influences.
Treatment options such as detoxification, rehabilitation therapy & support groups should be taken seriously to prevent negative consequences.
What Does It Mean To Be High On Drugs?
Being high on drugs describes the altered mental and physical states induced by substance use, ranging from euphoria and relaxation to hallucinations. According to the SAMSHA 2021 National Survey On Drug Use, 17.8% of individuals aged 12 and older have used illicit drugs in the past year, while 13.5% have used marijuana or hashish. Club drugs like MDMA, ecstasy, and ketamine, as well as synthetic drugs like K2 and Spice, are prevalent in social settings and are illegal in most states.
Recognizing the signs of drug use can help identify those struggling with addiction, thereby facilitating timely intervention and support. Withdrawal symptoms, including cravings and physical discomfort, often arise when attempting to quit, making it crucial to spot these signs for effective recovery support.
What Does A Drug High Do To The Brain?
Substances impact the brain and cause a high feeling by:
- Disrupting neuron communication
- Modifying brain regions including the basal ganglia, extended amygdala, and prefrontal cortex
- Triggering neurotransmitter surges, such as dopamine
These changes can worsen existing mental health conditions like PTSD. Long-term drug use leads to brain impairments, affecting daily functions, emotions, and behaviors. The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) categorizes drugs based on their abuse and addiction potential, underscoring the long-term risks involved.
Drugs can interfere with the proper functioning of neurotransmitters in the brain, resulting in alterations in mood, behavior, and perception. Some drugs, such as date rape drugs, can cause severe impairment in cognitive function and memory, making it difficult for victims to recall events or protect themselves. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that are naturally present in the brain. When individuals misuse drugs, they can disrupt the balance of these neurotransmitters, leading to a range of negative effects on mental and physical health.
Numerous drugs can drastically alter brain chemistry in different ways. For instance, they may disrupt the transmission of signals between neurons by adjusting the levels of neurotransmitters, leading to alterations in mood, emotions, behavior, and perception. Addictive drugs, for example, impact brain pathways associated with reward, like the dopamine system. Psychoactive drugs can elevate dopamine levels in the brain, which triggers various effects including:
rapid or rambling speech
increased energy and alertness
euphoria or intense pleasure
heightened sensory perception
distorted perception of time and space
Each drug’s impact on brain chemistry is unique, including the effects of other drugs.

10 Different Types Of Drugs And Their Highs
Identification of substance-specific symptoms involves recognizing the distinct signs related to stimulants, depressants, and hallucinogens. This knowledge can help spot signs of abuse in friends, family members, or coworkers and facilitate support for their recovery. Each drug has a unique impact on physical, behavioral, and psychological symptoms, underscoring the importance of understanding the specific signs associated with different substances.
1. Stimulant High

The stimulant high results in a range of observable physical and behavioral changes including increased energy and hyperactivity. While generally consistent across various stimulants like cocaine, amphetamine prescriptions, methamphetamine, and caffeine, these effects can vary in intensity based on the specific substance and dosage used. For instance, the intensity of heightened energy and confidence might be more pronounced with cocaine use compared to caffeine, but both substances can produce similar stimulant effects.
Different stimulants can also impact the brain’s reward system differently, leading to psychological dependency. This form of addiction involves craving the drug’s emotional or psychological effects, like increased sociability, in addition to physical dependence.
Signs of a Stimulant High:
- Heightened energy and alertness
- Restlessness or agitation
- Rapid speech and excessive talking
- Increased confidence and sociability
- Reduced appetite and weight loss
- Insomnia or difficulty sleeping
- Dilated pupils
- Impulsive or risky behavior
- Hyperactivity or fidgeting
- Paranoia or suspiciousness
Recognizing these signs is key for early intervention and support. The symptoms range from heightened alertness to paranoia, highlighting the significant impact stimulants have on the central nervous system. Identifying these signs can prompt friends, family members, or coworkers to offer support and encourage seeking professional help.
2. Opiate High

Opiates, derived from the opium poppy plant, are known for their potent pain-relieving properties and are commonly used both medically and recreationally. The high from opiates is characterized by profound relaxation, pain relief, and a sense of euphoria. However, these drugs also pose a high risk of addiction and can lead to severe physical and mental health issues.
Key Characteristics of an Opiate High:
- Profound Relaxation: A deep sense of calm and relaxation is a hallmark of opiate use.
- Euphoria: Users often experience a feeling of intense happiness or joy.
- Pain Relief: Opiates are effective at dulling physical pain, which contributes to their medical use.
- Drowsiness or Sedation: Opiates commonly cause users to feel sleepy or lethargic.
- Constricted Pupils: Known as miosis, this is a distinctive physical sign of opiate use.
- Slowed Breathing: Opiates depress the respiratory system, leading to shallow or slow breathing.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Especially in new users or at high doses.
- Itching: Users may experience itching or flushed skin.
- Constipation: A common side effect of prolonged opiate use.
Common Opiates Include:
- Morphine
- Heroin
- Codeine
- Oxycodone (OxyContin)
- Hydrocodone (Vicodin)
- Fentanyl
The euphoric and pain-relieving effects of opiates make them highly addictive, and their misuse can quickly lead to physical dependence and addiction. Recognizing these signs can be crucial in identifying opiate misuse and intervening early. The risk of overdose is particularly high with opiates, as they can significantly depress breathing. This makes awareness and understanding of opiate highs and their dangers essential for friends, family members, or coworkers to provide timely support and encourage professional help.
3. Depressant Drug High

Depressants are a class of drugs that reduce the activity of the central nervous system. They are often prescribed to treat anxiety, panic, acute stress reactions, and sleep disorders and cause a high typically characterized by relaxation, sedation, and reduced inhibition. However, these substances can be addictive and pose risks, especially when misused or combined with other substances like alcohol.Depressants are a class of drugs that reduce the stimulation of the central nervous system during the high. They include a range of substances from prescription medications like benzodiazepines and barbiturates to alcohol. The primary effect of depressants is to induce relaxation, decrease anxiety, and in higher doses, cause sedation.
Key Characteristics of a Depressant High:
- Relaxation and Calmness: A general sense of tranquility and relaxation is often experienced.
- Drowsiness and Sedation: Many depressants, especially in higher doses, lead to significant drowsiness or sedation.
- Slowed Reaction Time: Depressants can impair cognitive functions, leading to slower thought processes and reaction times.
- Slurred Speech: Speech may become slow and slurred, a sign of the drug’s impact on the central nervous system.
- Reduced Inhibitions: Similar to alcohol, depressants can lower inhibitions and lead to risk-taking behaviors.
- Impaired Coordination: Physical movements may become clumsy or uncoordinated.
- Difficulty Concentrating: Concentration and focus can be significantly diminished.
- Memory Impairment: Some depressants can affect short-term memory.
- Respiratory Depression: In high doses, depressants can dangerously slow down breathing, which is a significant risk for overdose.
Common Depressants Include:
- Alcohol
- Benzodiazepines (e.g., Xanax, Valium)
- Barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital)
- Sleep medications (e.g., Ambien, Lunesta)
While depressants can be prescribed for legitimate medical reasons, such as treating anxiety or insomnia, their misuse can lead to addiction and serious health issues. It’s important to recognize the signs of depressant use, as their sedative effects can dangerously compound, especially when mixed with other depressants like alcohol. Understanding these signs can help in identifying misuse and intervening appropriately. The risk of overdose, particularly respiratory depression, makes awareness and prompt action crucial.
The depressant use can lead to drowsiness, slurred speech, and slowed breathing. Depressants can reduce arousal and stimulation in the central nervous system, leading to increased sleep, relief of anxiety and muscle spasms, and prevention of seizures. They are known to slow down brain activity, which makes them useful for treating anxiety, panic, and sleep disorders. Short-term effects of depressant use on the body and brain include slowed brain function, slowed pulse and breathing, lowered blood pressure, poor concentration, confusion, fatigue, and dizziness.
Long-term use can lead to psychological dependence, tolerance, addiction, and severe withdrawal symptoms. It’s crucial to recognize the unique signs of depressant use, such as drowsiness, impaired memory performance, and changes in thinking or mental activity. Being aware of these symptoms can help identify individuals struggling with depressant use and provide support for recovery.
4. Hallucinogen and Psychadelic High

Hallucinogens and psychedelics are a class of drugs known for highs that cause profound changes in perception, mood, and thought. The high experience, often referred to as a “trip,” can vary greatly depending on the specific substance, dosage, and individual’s mindset and environment.
Key Characteristics of a Hallucinogen and Psychedelic High:
- Altered Perception: Users may experience intensified sensory experiences, such as vivid colors, patterns, and sounds.
- Hallucinations: These can be visual or auditory, where users see or hear things that aren’t there.
- Altered Sense of Time: Time may seem to slow down or speed up.
- Emotional Shifts: Rapid mood swings, from euphoria to introspection, or even anxiety and paranoia.
- Sense of Connectedness: Feelings of oneness with the universe or profound spiritual experiences.
- Synesthesia: A blending of senses, such as “seeing” sounds or “hearing” colors.
- Distorted Thinking: Disorganized thoughts, difficulty concentrating, or profound philosophical insights.
- Physical Effects: Nausea, increased heart rate, and changes in body temperature.
Common Hallucinogens and Psychedelics Include:
- LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide)
- Psilocybin (Magic Mushrooms)
- DMT (Dimethyltryptamine)
- Mescaline (found in Peyote and San Pedro cactus)
- Ayahuasca (a brew containing DMT)
- MDMA (Ecstasy, Molly) – although primarily a stimulant, it has psychedelic properties
The experience of using hallucinogens and psychedelics can be unpredictable and varies widely. Some users report life-changing insights or mystical experiences, while others may have challenging or frightening experiences, sometimes referred to as a “bad trip.” Due to their potent effects on perception and mood, it’s important to approach these substances with caution and be aware of their potential for causing psychological distress. Recognition of these symptoms can be vital for providing support to individuals who may have challenging experiences with these substances.
Hallucinogen or psychedelic highs cause perceptual distortions, emotional swings, and disorientation. The most commonly encountered hallucinogens are lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), phencyclidine (PCP), and psilocybin, or “magic mushrooms”. People on hallucinogens may display a range of behaviors, such as appearing drowsy, panicked, or at peace, depending on the type of “trip” they are having.
5. Inhalant High

Inhalants are a diverse group of substances that are sniffed or inhaled to achieve a quick high. They include everyday household products like solvents, aerosol sprays, gases, and nitrites, which are abused for their psychoactive effects. The high from inhalants is usually short-lived but can be very intense.
Key Characteristics of an Inhalant High:
- Immediate Euphoria: Users often experience a rapid onset of euphoria or a ‘rush’ immediately after inhalation.
- Dizziness and Lightheadedness: A common immediate effect, often accompanied by a sense of disorientation.
- Loss of Coordination: Difficulty in motor skills and unsteady movements.
- Slurred Speech: Similar to alcohol intoxication, inhalant use can lead to impaired speech.
- Hallucinations and Delusions: In some cases, especially with prolonged use or high concentrations.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often experienced due to the chemical nature of the substances.
- Coughing and Wheezing: Respiratory issues can occur due to the inhalation of fumes.
- Rapid Heart Rate: Some inhalants can cause a dangerous increase in heart rate.
- Sense of Excitement or Overactivity: Followed by a rapid decline in energy levels.
Commonly Abused Inhalants Include:
- Paint thinners and removers
- Gasoline
- Glue
- Aerosol sprays (such as spray paint, deodorant, hair spray)
- Nitrous oxide (“laughing gas” “whippits“)
- Butane lighters and propane tanks
- Nitrites (“poppers”)
Inhalant abuse is particularly risky because these substances are not intended for human consumption and can be toxic or even fatal. The effects are generally short-lived, leading users to repeatedly inhale to maintain the high, increasing the risk of harmful side effects or sudden death from “sudden sniffing death syndrome.” The use of inhalants is more common among younger individuals, making education and awareness particularly important in schools and among parents. Recognizing the signs of inhalant use can be crucial for timely intervention and prevention of serious health consequences.
6. Dissociative High

Dissociatives are a class of drugs that induce a state of detachment from reality, affecting perception, identity, and consciousness. Commonly used dissociatives include Ketamine, PCP (Phencyclidine), and DXM (Dextromethorphan), found in some cough syrups. These substances can lead to a range of experiences from mild detachment to profound dissociative states.
Key Characteristics of a Dissociative High:
- Altered Perception of Reality: Users may feel detached from their surroundings and themselves, experiencing a disconnection between mind and body.
- Visual and Auditory Hallucinations: Distorted perception of sights and sounds.
- Altered Sense of Time: Time may seem to slow down, speed up, or become irrelevant.
- Numbness: Physical sensations of numbness or reduced pain sensitivity.
- Euphoria or Bliss: A feeling of floating, tranquility, and well-being.
- Cognitive Impairments: Difficulty thinking clearly, memory lapses, and impaired judgment.
- Mood Swings: Rapid changes in emotional states, from euphoria to anxiety or depression.
- Motor Coordination Loss: Unsteady movements, difficulty walking or standing.
- Sense of Immortality or Superhuman Powers: Particularly with drugs like PCP.
Commonly Used Dissociatives:
- Ketamine: Used both as an anesthetic in medical settings and recreationally for its dissociative effects.
- Phencyclidine (PCP): Known for its potent and unpredictable effects, often leading to aggressive behavior in higher doses.
- Dextromethorphan (DXM): Found in some over-the-counter cough medicines, abused for its dissociative and hallucinogenic properties at high doses.
The use of dissociatives can be particularly disorienting and potentially dangerous, especially in unfamiliar or unsafe environments. Users must be in a safe setting if they choose to use these substances. The dissociative state can impair judgment and motor skills, increasing the risk of accidents. Prolonged or frequent use of dissociatives can lead to psychological dependence and long-term cognitive impairments. Recognizing the signs of dissociative drug use is important for providing appropriate support and intervention, particularly among young adults and teenagers who might be more susceptible to experimenting with these substances.
7. Club Drug High

Club drugs refer to a category of psychoactive substances commonly used in party, nightclub, and dance festival environments. These drugs are known for enhancing sensory perceptions, boosting energy, and promoting socialization. However, they also pose significant risks due to their unpredictable effects, potential for abuse, and dangerous interactions with other substances, including alcohol.
Key Characteristics of a Club Drug High:
- Euphoria and Enhanced Mood: Many club drugs elevate mood, creating a sense of happiness and well-being.
- Heightened Sensory Perception: Enhanced colors, sounds, and tactile sensations are common.
- Increased Sociability and Empathy: These drugs often lower inhibitions and increase feelings of closeness to others.
- Altered Perception of Time and Space: Users may experience a warped sense of reality.
- Increased Stamina and Energy: Some club drugs have stimulant-like effects, promoting prolonged dancing and activity.
- Visual and Auditory Hallucinations: Depending on the substance, users might experience mild to intense hallucinations.
- Disorientation and Confusion: Higher doses can lead to confusion and memory problems.
Commonly Used Club Drugs:
- MDMA (Ecstasy/Molly): Known for its stimulant and empathogenic effects, enhancing emotional and sensory experiences.
- GHB (Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid): Often used for its euphoric and sedative effects, but can be dangerous at high doses.
- Ketamine: Used for its dissociative and anesthetic properties, it can create a sense of detachment from reality.
- LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide): A powerful hallucinogen, causing significant alterations in perception and thought.
- Rohypnol (“Roofies”): A benzodiazepine, notorious for its use in drug-facilitated sexual assaults due to its incapacitating effects.
The use of club drugs, particularly in party settings, can be risky due to the combination of loud music, dehydration, physical exertion, and the crowded environment. These factors can exacerbate the drugs’ effects and increase the risk of adverse reactions. Additionally, the illicit nature of these drugs means that purity and dosage are often unknown, raising the risk of overdose. Recognizing the signs of club drug use can aid in early intervention, especially in environments where these substances are prevalent. It’s important for individuals and communities involved in nightlife to be aware of these drugs’ effects and the importance of safety measures and responsible behavior.
8. Cannabis High

Cannabis, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its psychoactive and medicinal properties. The primary psychoactive component is THC (tetrahydrocannabinol). The effects of cannabis can vary greatly depending on the strain, THC content, and individual user.
Key Characteristics of a Cannabis High:
- Euphoria and Relaxation: A sense of well-being and relaxation is commonly reported.
- Altered Perception: Enhanced sensory perception, such as vivid colors and intensified sounds.
- Increased Appetite: Often referred to as “the munchies.”
- Altered Time Perception: Time may seem to pass more slowly.
- Mood Changes: This can range from happiness and giddiness to anxiety or paranoia.
- Impaired Short-Term Memory: Difficulty in retaining and recalling recent information.
- Dry Mouth and Red Eyes: Common physical side effects.
- Coordination Issues: Impaired motor skills and reaction times.
9. Synthetic Stimulant (“Bath Salts”) High

Synthetic stimulants, often referred to as “bath salts,” mimic the effects of natural stimulant drugs like cocaine and amphetamines. These substances are known for their powerful psychoactive effects and high potential for abuse and adverse reactions.
Key Characteristics of a Synthetic Stimulant High:
- Intense Euphoria: Rapid onset of pleasure or euphoria.
- Increased Energy and Alertness: Similar to other stimulants like cocaine.
- Agitation and Paranoia: Can lead to aggressive behavior and delusions.
- Hallucinations: In some cases, users may experience visual or auditory hallucinations.
- Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure: Can be dangerous, leading to cardiovascular problems.
- Impulsivity: Engaging in risky or dangerous behaviors.
- Hyperthermia: Elevated body temperature, which can be life-threatening.
10. Synthetic Cannabinoids High

Synthetic cannabinoids, commonly known as “spice” or “K2,” are man-made chemicals that are designed to mimic the effects of THC. However, they often have unpredictable and hazardous effects.
Key Characteristics of a Synthetic Cannabinoid High:
- Elevated Mood: Some users experience mood enhancement.
- Altered Perception: Changes in perception, although often less pleasant than those experienced with natural cannabis.
- Rapid Heart Rate: More pronounced than with natural cannabis.
- Extreme Anxiety and Paranoia: Can be more severe compared to THC.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Especially in new users or at high doses.
- Confusion and Agitation: Can lead to aggressive behavior.
- Hallucinations and Psychotic Episodes: In severe cases, users may experience intense hallucinations and psychosis.
What Are The Common Symptoms of Being High on Drugs?
Typical symptoms of being high on drugs encompass physical signs like dilated pupils, behavioral modifications such as heightened energy or lethargy, and psychological symptoms like paranoia or euphoria. The manifestations of abuse can differ, contingent on the type of substance in question.
Club drugs, such as MDMA, ecstasy, or molly, GHB, ketamine, and flunitrazepam, are commonly used at clubs, concerts, and parties and can cause sedation, muscle relaxation, confusion, memory loss, and the potential for sexual misconduct or sexual assault. Synthetic drugs, like K2, Spice, and bath salts, are illegal in most states and can cause similar symptoms.
Drug abuse, including alcohol abuse, can manifest in a variety of physical signs, some of which are instantly noticeable, while others may be subtly concealed or appear as gradual changes. Adolescents using drugs may show signs such as:
red and droopy eyes
constricted pupils from marijuana use
dilated pupils if they have consumed alcohol
a flushed, reddened facial complexion
Physical signs of cocaine use may include:
Dilated pupils
Increased heart rate
Elevated blood pressure
Runny or bloody nose
Nosebleeds
Weight loss
Insomnia
Restlessness
Hyperactivity
Tremors or muscle twitches
Opioid use may be evidenced through physical signs such as:
pinpoint pupils
drowsiness or nodding off
slowed breathing
flushed or pale skin
track marks or needle puncture wounds
poor hygiene or neglect of physical appearance
Changes in behavior may include upheavals in energy levels, social interactions, and daily routines.
Observable behavioral signs of stimulant drug use can include:
An increase in energy and alertness
Restlessness or agitation
Rapid and excessive speech
A rise in confidence and social behavior
A decrease in appetite and weight
Sleep disturbances
Dilated pupils
Impulsive or risky behavior
Hyperactivity
Fidgeting
Paranoia or suspiciousness
However, it’s crucial to recognize that many signs of drug use are also indicative of mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety. Some behavioral changes that may indicate drug use in teens include:
Being overly loud and disruptive
Exhibiting inappropriate laughter
Exhibiting clumsiness
Appearing sullen and withdrawn
Appearing unusually tired
Having droopy eyelids
Appearing queasy
Having difficulty walking straight to the bathroom
It’s important to approach these common signs with care and seek professional help if needed.
Psychological effects of substance use can include:
Mood fluctuations
Uneasiness
Visual and auditory disturbances
Hallucinations
Delusions
Olfactory hallucinations
Anti-social behavior
Panic attacks
Confusion
Indications of recent use of substituted cathinones can include serious intoxication, which can lead to hazardous health outcomes or even death.
It is important to recognize that the psychological symptoms of drug use can be quite diverse, depending on the type of drug consumed and the individual’s unique reaction to the substance.
What Is The Role of Dopamine In A Drug High?
Dopamine plays a central role in reinforcing pleasurable activities and is implicated in the association between drug consumption, pleasure, and environmental cues which are enhanced during a drug high. Healthcare providers can use this information to better understand the mechanisms of addiction and develop effective treatment strategies. Different types of drug highs can have a range of effects on dopamine levels in the brain. Opioids, cocaine, and nicotine are known to cause a surge of dopamine in the reward pathway, resulting in feelings of pleasure and reinforcement of drug use. Additionally, amphetamines can increase the release of dopamine in the brain. Ultimately, drugs of abuse can disturb the natural balance of dopamine in the brain, which can lead to addiction and dependence.
The brain releases dopamine when drugs are consumed due to the stimulation of the brain’s reward pathway, particularly the mesolimbic dopamine system. This dopamine release reinforces the connection between drug use and feelings of pleasure and reward. Furthermore, the dopamine surge produced by drugs is far more intense than what is typically released in response to natural rewards such as food or sex.
The relationship between drug use, pleasure, and external cues is that dopamine plays a central role in reinforcing pleasurable activities and is involved in the connection between drug consumption, pleasure, and external cues.
How To Detect Drug Use in Adolescents?
To detect drug use in adolescents, one might need to notice changes in their mood, behavior, peer groups, and academic performance. The presence of alcohol or smoke can be identified through their breath, clothing, and hair. Distinguishing signs of drug use from common adolescent behavior can be challenging. Often, drug use signals underlying mental health issues, such as depression or anxiety. Keeping an eye on these signs can help in early identification and intervention.
If a parent suspects their child is using drugs, they should take appropriate measures to ensure the safety of their child. They should initiate a conversation with their child and ask pertinent questions such as “Have you been drinking, vaping, or using drugs?”.
Early intervention is imperative to guarantee the highest potential for successful rehabilitation.
What Are The Risk Factors for Addiction?
Addiction risk factors encompass genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and personal personality traits. Studies have found that genetics account for at least half of a person’s susceptibility to substance addiction. Environmental factors can substantially heighten the risk of substance abuse and addiction, with drug accessibility often facilitated by risky environments and peer pressure playing a significant role in promoting substance use. Poverty, trauma, and stress can also contribute to addiction. Early exposure to drugs and their availability in a person’s surroundings can likewise amplify the risk of substance abuse and addiction.
Impulsivity, sensation-seeking, and risk-taking are individual personality traits that can increase the risk of addiction. Initiating drug use during childhood or adolescence is associated with heightened risk of dependence on the substance.
When to Seek Professional Intervention and Treatment
Seek professional intervention and treatment when drug use becomes problematic, causing negative consequences in a person’s life or when early warning signs of addiction are present. A professional interventionist can facilitate the planning process and ensure the successful execution of the event. During an intervention, family and friends come together to have an open and honest discussion with the individual regarding the effects of addiction and request that the person accept treatment.
Early intervention is imperative to guarantee the highest potential for successful rehabilitation. Treatment should include both medical detoxification and therapy to tackle the fundamental problems associated with substance abuse.
What Are The Treatment Options for Substance Use Disorders?
Therapeutic options for substance use disorders, including alcohol addiction, encompass detoxification, inpatient and outpatient rehabilitation, therapy, and support groups. The likelihood of developing a substance use disorder, also known as ‘addiction liability’, depends on factors such as the method of consumption, brain effects, the speed at which effects manifest, and the potential to induce tolerance and withdrawal symptoms. Substance use disorder can significantly impair an individual’s physical and mental health, interpersonal relationships, overall well-being, and in severe cases, can be life-threatening.
When discussing substance use with a loved one, it is important to approach the conversation with care and understanding. Being aware of the available treatment options and the importance of early intervention can significantly improve the chances of successful recovery.
What are the causes of addiction?
Addiction is a complex condition caused by a combination of factors, including changes to brain chemistry from exposure to drugs or activities, aggressive behavior in childhood, neglect from guardians, experimenting with substances, access to drugs at school, poverty in the community, and peer pressure.
How can I tell if a family member is using drugs?
Look out for physical, behavioral and psychological changes which may suggest drug use. Pay close attention to the type of substance being abused and their associated signs and symptoms.
How can I recognize the signs of stimulant use?
Signs of stimulant use include increased energy, rapid speech, dilated pupils, heightened alertness, and agitation, so be aware of any changes in behavior or appearance that could indicate drug use.
What are the risk factors for addiction?
Risk factors for addiction include genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and individual personality traits such as impulsivity, sensation-seeking, and risk-taking, making it a complex and multi-faceted disorder.
How Is A Runner High Different From A Drug High?
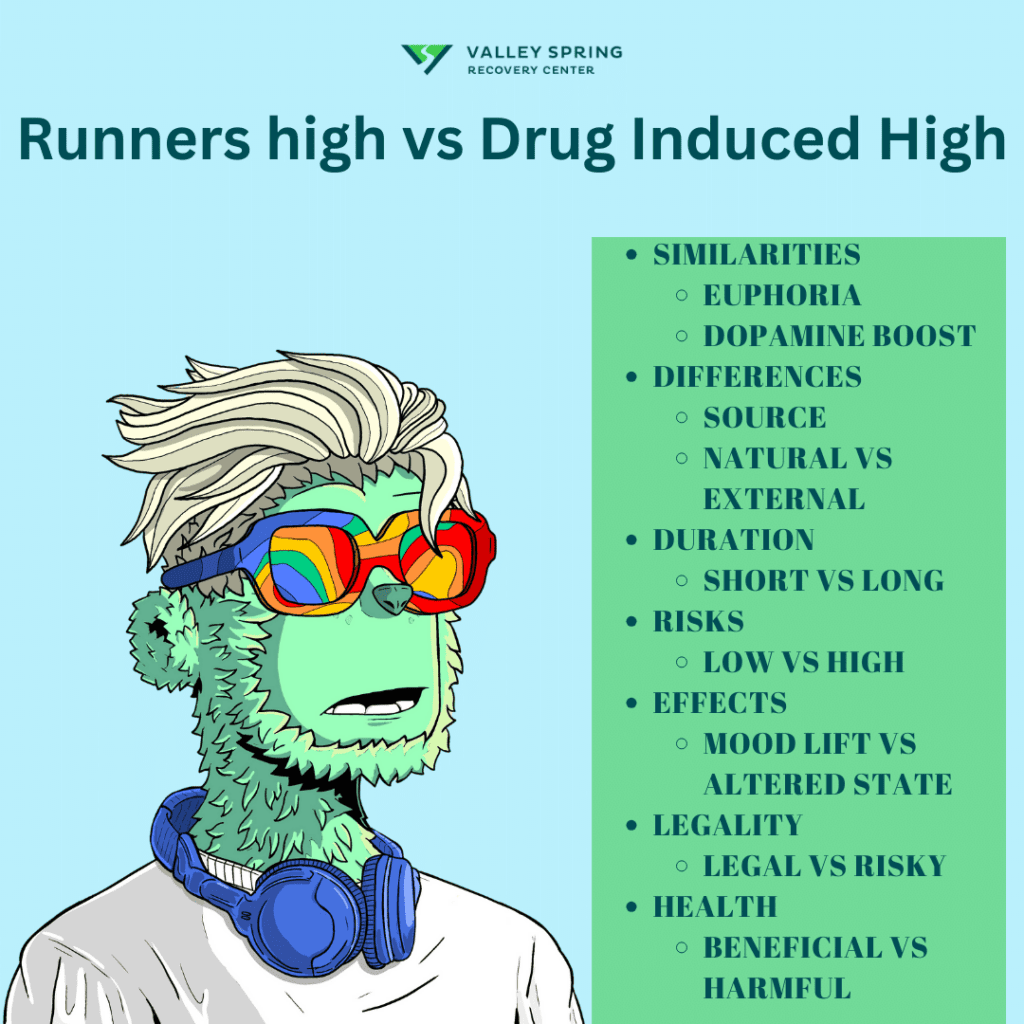
The term “runner’s high” is often used to describe a feeling of euphoria or a heightened state of well-being that some people experience after prolonged, vigorous exercise. This phenomenon is thought to be linked to the release of endorphins and other neurochemicals like endocannabinoids in the brain. These substances can act as natural painkillers and mood lifters, leading to feelings of happiness, reduced anxiety, and a decreased perception of pain.
While a “runner’s high” and the high experienced from drug use may share some similarities, such as increased dopamine levels and feelings of euphoria, there are also significant differences:
- Source: A runner’s high is induced by natural endorphins produced by the body during exercise, while drug-induced highs typically result from external substances that may mimic or alter natural neurotransmitter activity.
- Duration and Intensity: The duration and intensity of the high can differ significantly. Drug-induced highs may be more intense and longer-lasting depending on the substance used, the dosage, and individual factors.
- Risks and Side Effects: Drug use often comes with various risks and side effects, including the potential for abuse, addiction, and negative impacts on both mental and physical health. On the other hand, a runner’s high is generally considered to be a safe and healthy response to exercise.
- Psychological and Physical Effects: Some drugs can lead to altered perceptions, impaired judgment, and other cognitive changes, which are generally not associated with a runner’s high.
- Social and Legal Implications: Using illegal or prescription drugs for recreational purposes can have legal repercussions and can be socially stigmatized, whereas exercise and the associated runner’s high are socially accepted and encouraged.
- Overall Health Impact: Regular exercise like running has numerous well-documented health benefits, including cardiovascular health, weight management, and mental well-being, whereas frequent drug use often has the opposite effect on long-term health.
So while the feeling of a “runner’s high” and a drug-induced high might seem similar in terms of immediate emotional benefits, the causes, risks, and long-term effects can be quite different.
ion in cases of misuse. Synthetic substances, in particular, pose significant health risks due to their unpredictable nature and the potential for dangerous side effects.
Ben Fisher
All author postsShare This Post