Behavioral therapy, also known as behavior therapy, is a form of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and modifying specific behaviors, thoughts, and emotions that contribute to psychological distress or interfere with functioning. It is based on the principles of behaviorism and aims to replace maladaptive behaviors with more functional ones through evidence-based techniques.
Behavioral therapy has been an instrumental component of mental disorders treatment for decades and has been proven to be highly effective. A review of meta-analyses by Hofmann, S. G., et al (2012) examined the efficacy of CBT across different disorders, including anxiety disorders, depression, PTSD, and OCD. The findings indicated significant and robust effects of CBT in reducing symptoms and improving functioning.
What are the Types of Behavioral Therapy?
Behavioral therapy encompasses various approaches that focus on understanding and modifying human behavior. Some common types of behavioral therapy include:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive behavioral therapy is a widely used form of therapy that combines cognitive and behavioral techniques. It aims to identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to psychological distress.
2. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
DBT was initially developed to treat individuals with borderline personality disorder but has since been adapted for other conditions. It emphasizes skills training in areas such as emotional regulation, distress tolerance, interpersonal effectiveness, and mindfulness.
3. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA)
ABA is a systematic approach primarily used to address behavior issues in individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). It involves analyzing and modifying behavior through reinforcement techniques, shaping, prompting, and other strategies.
4. Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP is commonly utilized in the treatment of anxiety disorders, particularly obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). It involves gradually exposing individuals to feared situations or stimuli while preventing the associated compulsive behaviors.
5. Systematic Desensitization
This technique is employed to treat phobias and anxiety disorders. It involves systematically exposing individuals to feared stimuli or situations in a controlled and gradual manner, allowing them to develop relaxation and coping skills.
6. Token Economy
Token economy is often used in settings such as schools or psychiatric hospitals to reinforce desired behaviors. It involves providing tokens or rewards that can be exchanged for privileges or desired items when individuals exhibit positive behaviors.
7. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) is a form of psychotherapy that combines acceptance and mindfulness strategies with commitment and behavior-change strategies. The goal of ACT is to help individuals accept the difficulties that come with life, be present, and commit to actions that enrich their lives and align with their values.
These are just a few examples, and there are other specialized forms of behavioral therapy tailored to specific conditions or populations. The choice of therapy depends on the individual’s needs and the expertise of the therapist.
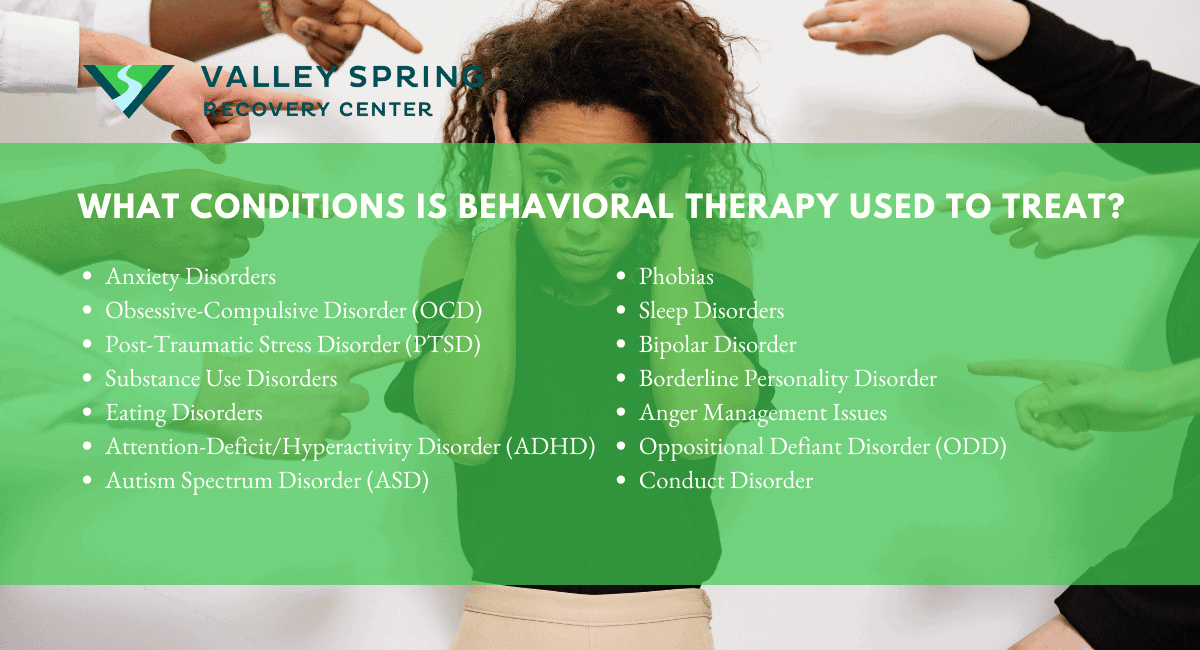
What Conditions is Behavioral Therapy Used to Treat?
Behavioral therapy can be used to treat a wide range of mental health conditions and behavioral issues. Some of the common conditions for which behavioral therapy is often utilized include:
- Depression
- Anxiety Disorders
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Substance Use Disorders
- Eating Disorders
- Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Phobias
- Sleep Disorders
- Bipolar Disorder
- Borderline Personality Disorder
- Anger Management Issues
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)
- Conduct Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Social Anxiety Disorder
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Panic Disorder
- Specific Phobias
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder
- Hoarding Disorder
- Trichotillomania (Hair-Pulling Disorder)
- Excoriation (Skin-Picking) Disorder
- Tic Disorders (e.g., Tourette’s Syndrome)
- Adjustment Disorders
- Insomnia
- Chronic Pain
- Sexual Dysfunction
- Gambling Addiction
What are the Techniques of Behavioral Therapy?
Behavioral therapy utilizes various techniques to understand and modify behaviors. Here are some common techniques used in behavioral therapy:
- Operant Conditioning: This technique focuses on modifying behavior through reinforcement and punishment. It involves providing positive reinforcement (rewards) to increase desired behaviors and implementing negative consequences (punishment) to decrease unwanted behaviors.
- Behavior Analysis: Behavior analysis involves assessing and understanding the antecedents (triggers) and consequences of a behavior. By identifying the factors that influence behavior, therapists can develop strategies to modify and shape behavior effectively.
- Behavior Modification: Behavior modification techniques involve implementing specific strategies to promote behavior change. This may include setting goals, tracking behavior, providing feedback, and utilizing reinforcement or punishment to encourage desired behaviors or discourage unwanted behaviors.
- Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is used to treat anxiety disorders and phobias. It involves gradually exposing individuals to feared situations or stimuli in a controlled and safe manner, allowing them to learn that their fears are unfounded or manageable.
- Systematic Desensitization: This technique is a form of exposure therapy used to treat phobias and anxiety disorders. It involves gradually exposing individuals to feared stimuli while pairing relaxation techniques to reduce anxiety and fear responses.
- Modeling: Modeling involves demonstrating and teaching desired behaviors through observation and imitation. By observing positive role models, individuals can learn and acquire new skills or behaviors.
- Token Economy: Token economy is a behavior modification technique often used in settings such as schools or psychiatric hospitals. It involves providing tokens or rewards (e.g., points, tokens, stickers) that can be exchanged for privileges or desired items when individuals exhibit positive behaviors.
- Social Skills Training: Social skills training focuses on teaching individuals specific social skills and behaviors to improve their interpersonal interactions and relationships. This may involve role-playing, communication exercises, and feedback to develop appropriate social skills.
- Relaxation Training: Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery, are utilized to help individuals manage stress, anxiety, and physical tension.
- Behavioral Contracts: Behavioral contracts involve creating written agreements between individuals and therapists or other parties to outline specific behavioral goals, consequences, and rewards. They provide clear expectations and accountability for behavior change.
- Self-Monitoring: Self-monitoring involves individuals tracking and recording their own behaviors, thoughts, or emotions. This technique increases self-awareness and provides valuable data for identifying patterns, triggers, and progress.
- Reinforcement Schedules: Different reinforcement schedules, such as continuous reinforcement (rewarding every instance of the desired behavior) or intermittent reinforcement (rewarding some instances of the behavior), can be used to shape and maintain behaviors.
These techniques can be used individually or in combination, depending on the needs and goals of the individual receiving therapy. The specific techniques employed will vary based on the therapist’s approach and the nature of the behavior being addressed.
What are the Benefits of Behavioral Therapy?

Behavioral therapy offers several benefits for individuals seeking treatment for various mental health conditions and behavioral issues. Some of the key benefits of behavioral therapy include:
1. Focus on Concrete Strategies
Behavioral therapy provides practical and actionable strategies to address specific behaviors and symptoms. It emphasizes identifying and modifying the factors that contribute to problematic behaviors, allowing individuals to develop healthier and more adaptive responses.
2. Empowerment and Self-Management
Behavioral therapy empowers individuals by teaching them skills and techniques to manage their own behaviors and emotions. It promotes self-awareness, self-control, and self-efficacy, enabling individuals to take an active role in their own treatment and personal growth.
3. Evidence-Based Approach
Behavioral therapy is grounded in scientific research and has a strong evidence base supporting its effectiveness. Many behavioral techniques have been extensively studied and shown to be beneficial in treating a wide range of mental health conditions.
4. Targeted and Goal-Oriented
Behavioral therapy is highly focused on specific goals and behaviors. It helps individuals identify and prioritize the behaviors they want to change, allowing for a more targeted and efficient treatment approach.
5. Practical and Applicable in Daily Life
Behavioral therapy techniques are designed to be practical and applicable in real-life situations. Individuals can easily implement what they learn in therapy into their daily lives, leading to tangible improvements and lasting change.
6. Collaboration and Active Participation
Behavioral therapy involves active collaboration between the therapist and the individual. It encourages individuals to actively participate in their treatment process, providing input, setting goals, and making decisions together with the therapist.
7. Versatility and Adaptability
Behavioral therapy can be adapted to various age groups, populations, and conditions. It can be tailored to meet the specific needs of individuals, ensuring that treatment approaches are personalized and effective.
8. Holistic Approach
Behavioral therapy takes a holistic view of individuals, considering the interplay between thoughts, behaviors, emotions, and environmental factors. It addresses the underlying factors contributing to behaviors, promoting overall well-being and functioning.
9. Long-Term Benefits
Behavioral therapy focuses on equipping individuals with skills and strategies that can be applied beyond the therapy sessions. It aims to promote long-term behavior change and provide individuals with tools to navigate challenges even after therapy concludes.
10. Complementary to Other Treatments
Behavioral therapy can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with other interventions, such as medication or other forms of therapy. It can enhance the effectiveness of other treatments and provide a comprehensive approach to care.
It’s important to note that the specific benefits experienced can vary depending on the individual, their unique circumstances, and the nature of the condition being treated. The effectiveness of behavioral therapy also relies on the expertise and rapport between the individual and the therapist.
How Effective is Behavioral Therapy For Addiction?
Behavioral therapy has been widely studied and shown to be effective in treating various mental health conditions like addiction and behavioral issues. A paper by Butler, A. C., et al (2006) titled “The empirical status of cognitive-behavioral therapy: A review of meta-analyses.” reviewed multiple studies and found strong empirical support for the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in treating various mental health conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, and substance use disorders.
The effectiveness of behavioral therapy can vary depending on factors such as the specific condition being treated, the individual’s unique circumstances, and the quality of the therapeutic relationship. However, overall, behavioral therapy has demonstrated positive outcomes in numerous research studies and clinical applications.
Here are some key points regarding the effectiveness of behavioral therapy:
1. Evidence-Based Approach
Behavioral therapy is supported by a robust body of scientific evidence. Many behavioral techniques have been extensively researched and found to be effective in treating a wide range of conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), eating disorders, substance use disorders, and more.
2. Specificity and Targeted Treatment
Behavioral therapy focuses on addressing specific behaviors and symptoms. By targeting and modifying these behaviors, individuals can experience significant improvements in their condition and quality of life.
3. Short-Term and Long-Term Benefits
Behavioral therapy often yields positive results in a relatively short period. Depending on the individual and the nature of the condition, noticeable improvements can be seen in as few as five to 20 sessions. Moreover, the skills and strategies learned in behavioral therapy can have long-lasting effects, helping individuals sustain positive changes beyond the duration of therapy.
4. Versatility and Adaptability
Behavioral therapy can be adapted and tailored to meet the needs of various populations, age groups, and conditions. It offers flexibility in treatment delivery, allowing for individualized approaches that maximize effectiveness.
5. Complementary to Other Treatments
Behavioral therapy can be used as a standalone treatment or in conjunction with other interventions, such as medication or other forms of therapy. It can enhance the effectiveness of other treatments and provide a comprehensive approach to care.
6. Real-World Application
Behavioral therapy techniques are designed to be practical and applicable in individuals’ daily lives. The skills acquired in therapy can be used in real-world situations, empowering individuals to manage their symptoms and improve their functioning outside of therapy sessions.
What is the Difference Between Behavioral Therapy and Psychoanalysis?
Behavioral therapy and psychoanalysis are two distinct approaches to psychotherapy. Behavioral therapy is based on behaviorism and focuses on modifying specific behaviors and thought patterns in the present. It utilizes techniques such as behavior modification, cognitive restructuring, and skills training. The therapy is typically shorter-term and goal-oriented, aiming to alleviate distress and improve functioning through evidence-based strategies.
On the other hand, psychoanalysis is rooted in psychodynamic theory and explores unconscious determinants of behavior, early life experiences, and unconscious motivations. It employs techniques like free association, dream analysis, and interpretation of transference. Psychoanalysis aims to bring about long-term personality change by gaining insight into the individual’s inner world and addressing unresolved conflicts.
Behavioral therapy emphasizes observable behaviors and the use of structured interventions, while psychoanalysis focuses on unconscious processes and the therapeutic relationship. Behavioral therapy is more focused and time-limited, while psychoanalysis is typically longer-term and more intensive. The therapeutic approach and techniques used in each modality differ significantly.
How Does Behavioral Therapy Work When Mental Health Disorders Are Present and Co Occur With Substance Use Disorder?
Behavioral therapy plays a crucial role in treating individuals where mental health disorders co-occur with Substance Use Disorder (SUD). This concurrent presence, often referred to as dual diagnosis, requires a comprehensive treatment approach. Here’s how behavioral therapy works in such cases:
- Integrated Treatment Approach: Behavioral therapy in cases of co-occurring disorders often involves an integrated treatment plan that addresses both the SUD and the mental health disorder simultaneously. This approach is more effective than treating each disorder separately.
- Identification of Interconnected Symptoms: Therapists work to understand how the symptoms of each disorder interact with and influence each other. For instance, substance use might be a coping mechanism for symptoms of a mental health disorder, and vice versa.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is commonly used to treat co-occurring disorders. It helps patients identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. This is particularly effective as it addresses issues like anxiety, depression, or PTSD, which often co-occur with SUD.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): DBT is effective in managing intense emotions and reducing self-harmful behaviors. It’s particularly useful for individuals with borderline personality disorder or those who engage in self-harm or suicidal behaviors alongside substance abuse.
- Motivational Interviewing: This technique enhances an individual’s motivation to change. It’s beneficial in cases where ambivalence about treatment or change is a barrier to recovery from both mental health and substance use issues.
- Relapse Prevention Training: Behavioral therapy emphasizes skills for managing cravings and avoiding triggers. For those with dual diagnoses, strategies are also developed to cope with symptoms of their mental health disorder without resorting to substance use.
- Holistic Therapies: Approaches like mindfulness, stress management, and relaxation techniques are often incorporated to help manage symptoms of both mental health and substance use disorders.
- Psychoeducation: Educating patients about their conditions, the effects of substances, and coping strategies is crucial. It empowers them to understand and manage their disorders effectively.
- Family Therapy: Involving family members can provide additional support, improve communication, and address familial patterns that may contribute to or exacerbate the disorders.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment: Therapy for co-occurring disorders requires ongoing evaluation. Treatment plans are regularly adjusted based on the individual’s progress and changing needs.
Ben Fisher
All author postsShare This Post