The issue of drug abuse transcends geographic boundaries, affecting societies on a global scale. Addiction statistics show that in the United States alone, approximately 21 million people struggle with substance use disorders, highlighting how widespread and impactful this issue can be according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
Drug addiction is a complex medical condition marked by the persistent and compulsive use of a substance, despite the harm it inflicts on physical health, emotional well-being, and relationships along with psychological and mental health. Substance use disorder changes the brain’s structure and function due to repeated drug use affecting the mind, body, emotions and spirit of the addicted individual and their loved ones.

The effects, impact, and consequences of substance abuse on an individual’s well-being can be grave and even life-threatening, manifesting in both immediate and prolonged ways and also affecting friends families, acquaintances, and colleagues that come into contact with the individual abusing substances.
Immediate repercussions entail disorientation, unclear articulation, difficult respiration, elevated cardiac rhythm and hypertension, motor skill challenges, mood fluctuations, apprehension, episodes of panic, or delusional thinking. Additionally, one may experience focus deficits, signs of withdrawal, compromised decision-making, heightened irritability, aggressive behavior, shifts in eating habits, sleep disturbances, and memory lapses.
Long-term effects of addiction target emotional well-being, social standing, financial impact, physical consequences, and mental health deterioration.
If you or a loved one are battling addiction to any kind of drug, you may experience a combination or all of the effects of drug abuse mentioned.
What Are The Effects Of Drug Addiction?

Drug addiction affects nearly every aspect of an individual’s life, spanning from physical and psychological health to social and economic consequences. Here’s a holistic overview of the multifaceted effects of drug addiction:
- Physical Health: Chronic drug use can lead to a myriad of health problems, including liver damage, respiratory distress, heart problems, and neurological damage. Substances like opioids and methamphetamines increase the risk of infectious diseases due to shared needles and unsafe practices according to Hodder SL, Feinberg J, Strathdee SA, et al.’s 2021 study titled The opioid crisis and HIV in the USA: deadly synergies.
- Psychological Impact: Addiction severely affects mental health, associated with an increased incidence of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety, cognitive impairments, and, in severe cases, psychosis. Neurological changes can lead to long-term behavioral and emotional alterations according to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMSHA); 2014. (Treatment Improvement Protocol (TIP) Series, No. 57.)
- Social Relationships: Substance dependency strains relationships, often leading to social withdrawal, conflicts with loved ones, and disrupted family dynamics. Neglectful parenting due to drug use can impact the emotional and psychological development of children according to the 2017 CBHSQ Report by Lipari, R.N. and Van Horn, S.L. titled Children living with parents who have a substance use disorder by the Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality department of Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMSHA).
- Economic Consequences: Addiction can cause financial instability as individuals may lose their ability to maintain employment. The costs associated with obtaining drugs, potential legal fines, and healthcare due to addiction-related illnesses can be substantial according to Miller, T. and Hendrie, D’s 2008 research study Substance Abuse Prevention Dollars and Cents: A Cost-Benefit Analysis, in the Center for Substance Abuse Prevention, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
- Legal Issues: Drug abuse can result in legal consequences, including arrests, fines, and jail time. These legal problems often complicate personal and professional lives, perpetuating a challenging cycle (U.S. Department of Justice, 2017).
- Risk of Overdose: One of the most immediate and severe risks of drug addiction is the potential for overdose, which can result in permanent health damage or death, particularly with potent substances like opioids (National Institutes of Health, 2021).
Addressing drug addiction requires comprehensive treatment programs that involve medical care, psychological support, and social services to not only tackle the immediate health issues associated with drug use but also the underlying factors contributing to addiction. This supports long-term recovery and reintegration into society (World Health Organization, 2020).
What are the effects of drug addiction on physical health?
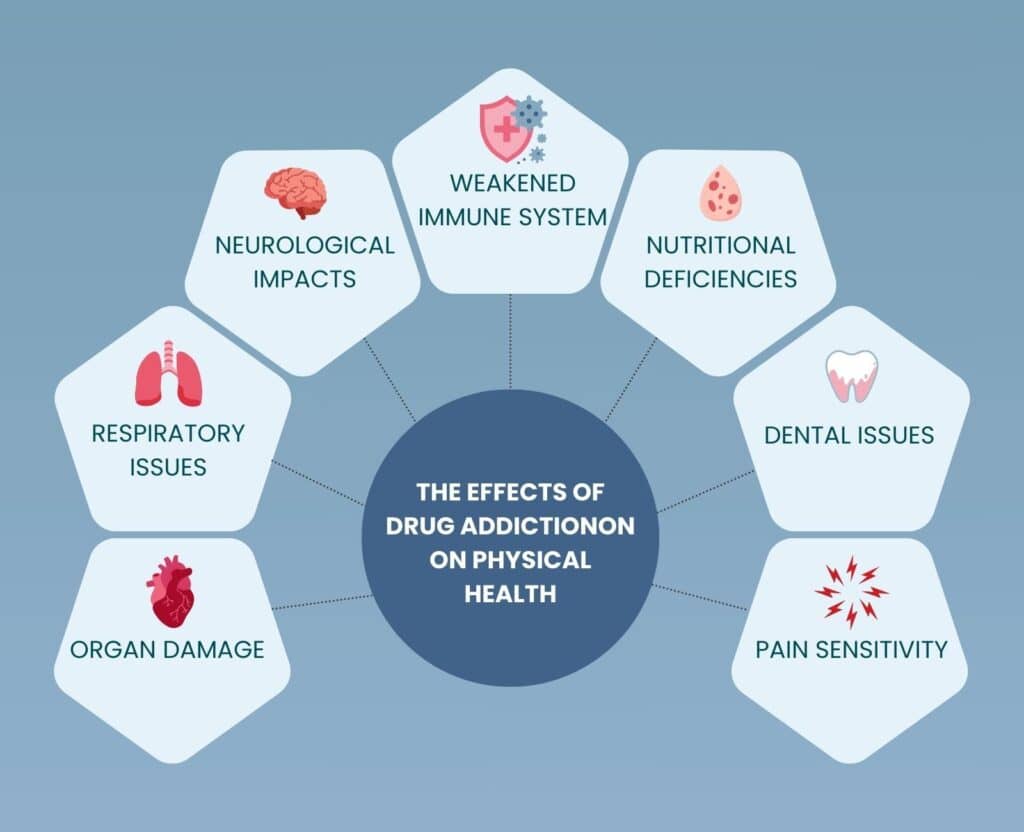
Drug abuse has a severe effect on physical health, if substances like opioids, stimulants, or even alcohol are overused for some time. The physical health impacts of substance misuse are listed below:
1. Organ Damage
Many drugs, whether they are illicit substances or prescription medications, can harm vital organs. For instance, long-term alcohol abuse can lead to liver cirrhosis, while drug abuse like cocaine or amphetamines can strain your heart, potentially leading to heart attacks or irregular heart rhythms.
2. Respiratory Issues
Smoking drugs like marijuana or crack cocaine can damage your respiratory system, leading to chronic bronchitis or lung infections. Intravenous drug use, like injecting heroin, increases the risk of blood-borne infections like HIV and hepatitis.
3. Neurological Impacts
Drug abuse can profoundly affect your brain. For example, opioids can slow down your breathing to dangerous levels, and the use of amphetamines or cocaine can cause seizures or strokes. Long-term drug abuse can also result in cognitive impairments and memory problems.
4. Weakened Immune System
Substance abuse can weaken your body’s immune defenses, making you more susceptible to infections. This means that you may get sick more often and take longer to recover.
5. Nutritional Deficiencies
Drug addiction can lead to poor dietary choices and a lack of interest in food, resulting in nutritional deficiencies. This can further weaken your immune system and overall physical health.
6. Dental Issues
Drug abuse negatively impacts oral health causing dental issues. For instance, methamphetamine use is notorious for causing “meth mouth,” a condition characterized by severe dental problems, including tooth decay and loss.
7. Pain Sensitivity
Opioid abuse can alter your perception of pain, making you more sensitive to discomfort. Paradoxically, this can lead to the abuse of even more opioids in an attempt to alleviate pain, creating a dangerous cycle.
What are the effects of addiction on pupil size in the eye and dilated pupils?
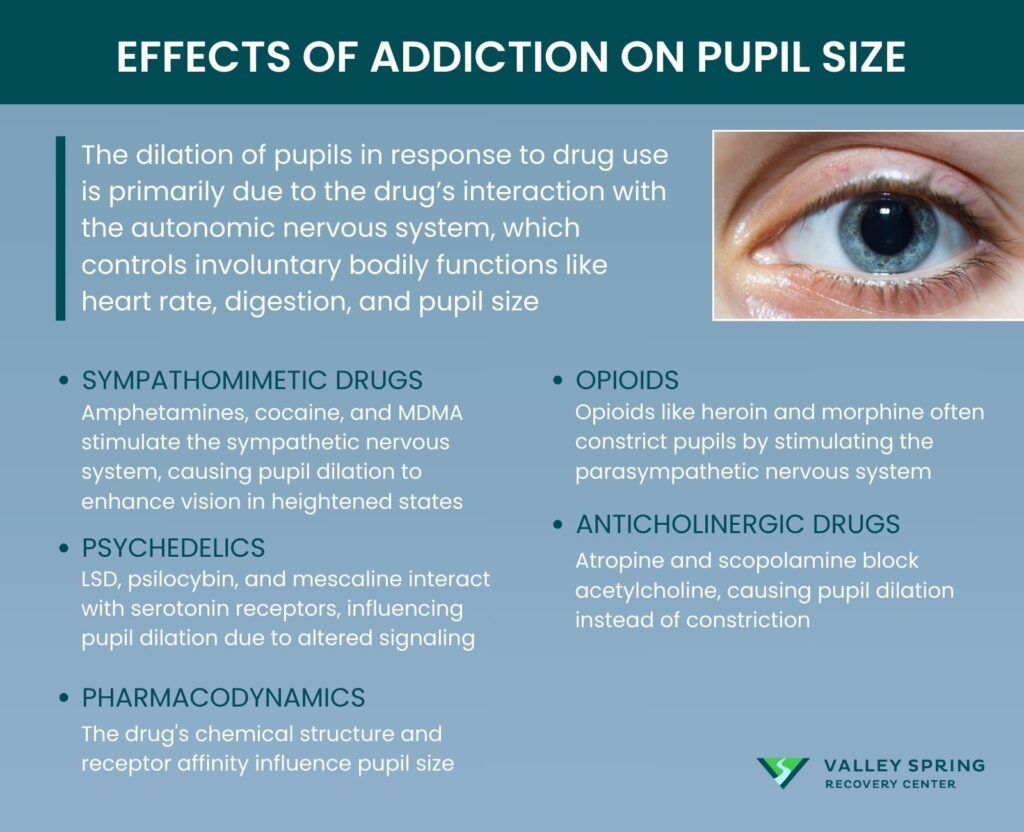
The dilation of pupils in response to drug use is primarily due to the drug’s interaction with the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions like heart rate, digestion, and pupil size. Drugs can either stimulate or inhibit the autonomic nervous system, leading to various physiological changes, including altered pupil size.
- Sympathomimetic Drugs: Substances like amphetamines, cocaine, and MDMA stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “fight or flight” response. This stimulation leads to the release of neurotransmitters like adrenaline, which among other things, causes the pupils to dilate to allow more light in, ostensibly to improve vision during a heightened state of alertness.
- Psychedelics: Drugs like LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline interact with serotonin receptors in the brain. Serotonin plays a role in regulating pupil size, and the alteration in its signaling can lead to dilated pupils.
- Opioids: Interestingly, opioids like heroin and morphine typically cause the pupils to constrict rather than dilate. This is because they stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for “rest and digest” functions.
- Anticholinergic Drugs: Substances like atropine and scopolamine block the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that usually causes pupils to constrict. By blocking its action, these drugs cause the pupils to dilate.
- Pharmacodynamics: The chemical structure of the drug and its affinity for certain receptors also play a role in how it affects pupil size.
What Are The Psychological Effects of Drug Addiction?
The psychological effects of addiction vary depending on the type of drug misuse and individual factors like pre-existing mental health conditions. Insights from the 2014 NIH study “Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction,” highlights the transformative effect of drugs on the brain and behavior, emphasizing addiction as a brain disease with significant psychological components.
Drug addiction profoundly impacts psychological health, manifesting a range of effects that disrupt both cognitive and emotional functioning. Cognitive impairments due to addiction involve challenges with decision-making, memory, and the ability to learn new information. These issues stem from neuroplastic changes in the brain, particularly in areas involved in reward, stress, and self-control, which are influenced heavily by substances of abuse.
Emotionally, individuals grappling with addiction may experience heightened levels of anxiety, depression, and mood instability. The use of substances can initially mask these problems, but over time, as the brain’s structure and function continue to be altered by drugs, these mental health issues can become more severe. The chronic nature of addiction can lead to a cycle where the individual’s emotional state depends heavily on the presence or absence of the drug, further complicating recovery efforts.
The interaction between drug use and psychological health is complex. Substance abuse can exacerbate existing mental disorders and may even contribute to the development of new psychiatric conditions. This bidirectional relationship underscores the importance of addressing both addiction and mental health simultaneously in treatment settings to enhance recovery outcomes and reduce the risk of relapse.
The common mental and psychological and mental effects of addiction are far-reaching and treatment approaches must adapt to treat symptoms.
How Does Drug Addiction Increase Mental Health Conditions?
Drug addiction often goes hand in hand with mental health issues like anxiety and depression. The substances may provide temporary relief, but they worsen these conditions in the long run, creating a vicious cycle.
What Effects Does Addiction Have On Brain Function?
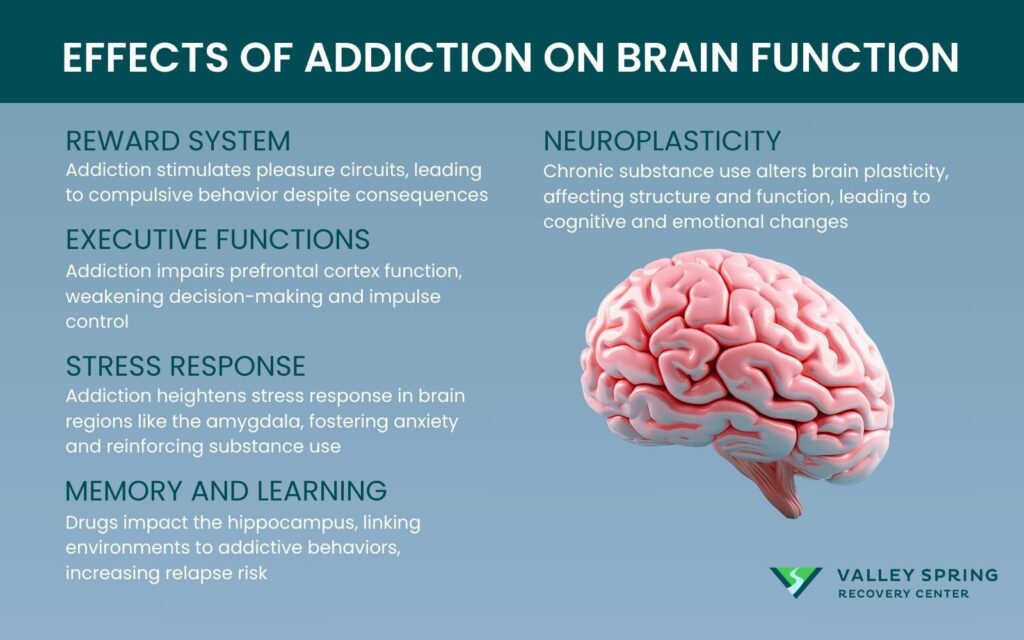
Addiction significantly impacts brain function by altering the brain’s natural balance of neurotransmitters, particularly those related to reward, motivation, learning, and memory. Here’s how addiction affects various aspects of brain function:
- Reward System: Addiction typically involves substances or behaviors that provide an intense sense of pleasure. These activities stimulate the brain’s reward system, particularly through the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. Over time, the brain’s reward circuits become overly engaged, leading to the compulsive seeking and use of addictive substances or behaviors despite adverse consequences.
- Executive Functions: The prefrontal cortex, responsible for decision-making, impulse control, and self-regulation, is also affected. As addiction progresses, it can diminish the ability to make sound decisions and resist impulses, making it increasingly difficult for individuals to abstain from the substance or behavior they are addicted to.
- Stress Response: Addiction alters the brain regions involved in stress regulation, such as the amygdala. This change can lead to increased sensitivity to stress, often resulting in anxiety and irritability when the individual is not using the substance. This altered stress response can perpetuate the addiction cycle as individuals seek relief from these unpleasant feelings through further substance use.
- Memory and Learning: Drugs can also affect the hippocampus, which plays a significant role in forming new memories. As a result, individuals may develop strong associations between certain environments, people, or events and their addictive behaviors, which can trigger cravings and make relapse more likely even after long periods of abstinence.
- Neuroplasticity: Chronic exposure to addictive substances can lead to alterations in brain plasticity, resulting in long-term or permanent changes to the neural pathways and circuits. These changes can affect not just the brain’s structure but also its function, potentially leading to cognitive impairments and altered emotional responses.
The effects of addiction on the brain are important to understand to develop effective treatments for addiction, which often involve medications to balance brain chemistry, behavioral therapies to modify behaviors, and support systems to help individuals cope with the emotional and psychological challenges of recovery.
How Does Cognitive Impairment Occur as a result of substance use?
Prolonged drug use can impair your cognitive functions, making it difficult to think clearly, make decisions, and focus on tasks. It’s like a fog that clouds your mind.
Why Does Substance Use Disorder Increase Paranoia and Hallucinations?
With some drugs, like methamphetamine or hallucinogens, addicts experience intense paranoia, hallucinations, or delusions. Substance misuse is notably higher among individuals with mental health issues, particularly those with psychosis than in the general population, with significant lifetime prevalence rates in those with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder (McCreadie, 2002; Regier et al., 1990). While the causal link between substance use and the onset of psychosis remains debated, substance misuse exacerbates the course of psychosis, leading to more severe outcomes including non-adherence to treatment, increased suicide risk, and poorer prognosis. The relationship between psychosis and substance misuse is complex, often entailing overlapping issues seen with substance misuse alone.
What Are The Effects Of Addiction On Emotions?

Drug addiction profoundly impacts emotional well-being, leading to increased anxiety, depression, and mood swings. It fosters feelings of guilt, shame, and loneliness while diminishing self-esteem and causing isolation from loved ones. These emotional effects complicate recovery, necessitating comprehensive treatment.
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Psychiatry found that individuals with substance use disorders are significantly more likely to suffer from mood and anxiety disorders. Specifically, the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC) reveals that about 20% of those with a mood disorder also have a co-occurring substance use disorder, while approximately 18% of individuals with an anxiety disorder struggle with addiction as well.
Furthermore, research indicates that the emotional toll of addiction can exacerbate the cycle of substance abuse. According to the American Psychological Association (APA), feelings of depression and anxiety can increase the likelihood of substance use as individuals turn to drugs or alcohol as a form of self-medication. This, in turn, leads to a worsening of emotional well-being, creating a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break.
Moreover, a study in the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence highlighted the significant role of guilt and shame in the context of addiction recovery. It found that higher levels of shame were associated with poorer outcomes in substance abuse treatment, underscoring the need for therapeutic interventions that specifically address these emotional states.
These statistics and studies underscore the complex relationship between drug addiction and emotional health, highlighting the necessity for integrated treatment approaches that address both the substance use disorder and the accompanying emotional effects of addiction to facilitate a more effective and sustainable recovery.
What Are The Effects of Drug Abuse On Mood?
Drug addiction can lead to severe mood swings, making it challenging to maintain stable relationships. You might feel irritable, anxious, or even aggressive when you can’t access the drug. Treating co-occurring mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorders, alongside substance use disorders can significantly improve patient outcomes by reducing substance cravings and enhancing recovery. Effective diagnosis involves methodical screening to distinguish between symptoms of mood disorders and those of substance abuse effects. Integrating psychotherapeutic interventions with medications proven effective for co-occurring disorders is vital. Increased collaboration between substance abuse and mental health professionals is key to better managing these complex conditions, as research indicates that addressing either condition can positively impact the overall recovery process.
What Are The Effects Of Addiction On Social Standing and Personal Finance?

The impact of drug addiction extends far beyond the individual, affecting both social relationships and economic stability. Drug addiction can strain your relationships with your loved ones, lead to legal troubles, disrupt employment, and create significant financial challenges that you may not be able to get out of:
1. Social Effects
- Strained Relationships: Drug addiction often strains your relationships with family and friends. People close to you may feel hurt, betrayed, or frustrated by your drug use, leading to conflicts and sometimes even estrangement.
- Isolation: As your addiction progresses, you may start to isolate yourself from loved ones. This isolation can lead to feelings of loneliness, which can worsen your addiction and mental health.
- Legal Consequences: Drug addiction can result in legal issues, including arrests and convictions. Legal troubles can lead to fines, probation, or even incarceration, further disrupting your life and future prospects.
- Financial Struggles: Supporting a drug addiction can be financially crippling. Money that could be used for essentials like housing, food, and healthcare often ends up being spent on drugs, leading to financial instability and debt.
- Impact on Parenting: If you have children, drug addiction can affect your ability to care for them. Child custody issues can arise, and children may be placed in foster care if their safety is at risk.
2. Economic Effects
- Loss of Employment: Maintaining steady employment can be challenging when dealing with drug addiction. Frequent absenteeism, impaired performance, or legal issues can lead to job loss.
- Educational Setbacks: For students battling addiction, educational goals may suffer. Absences, declining grades, or dropping out of school can disrupt your long-term prospects.
- Healthcare Costs: Treating health issues related to drug addiction can be costly. Hospitalizations, rehabilitation programs, and medications add to the financial burden.
- Crime and Criminal Justice Costs: Drug-related crimes, such as theft or drug trafficking, can lead to arrests and incarceration, incurring significant costs for the criminal justice system.
- The burden on Social Services: Drug addiction places strain on social services, including substance abuse treatment centers, emergency shelters, and welfare programs, which can affect funding and resources available for those in need.
What are drug addiction effects on relationships?

Drug addiction can have profound and far-reaching effects on relationships, impacting family, friendships, romantic partnerships, and professional interactions. Here are some ways in which drug addiction affects relationships:
- Trust Erosion: Substance addiction often leads individuals to engage in dishonest or secretive behavior, such as lying about their drug use or hiding substances. This behavior can erode trust between partners, family members, and friends, which is fundamental to healthy and stable relationships.
- Communication Breakdown: Addiction can cause individuals to withdraw or isolate themselves, impairing communication within relationships. Misunderstandings and lack of emotional availability can further strain interactions and discourage open dialogue.
- Financial Strain: Maintaining an addiction can be costly, leading to financial stress within families or between partners. Mismanagement of funds may include spending savings or accruing debt, which can ignite conflicts and resentment in relationships.
- Emotional Distress: The erratic behavior associated with addiction can be emotionally draining for loved ones. Partners and family members may experience a range of difficult emotions, including fear, sadness, anger, and frustration, which can affect their own mental health and well-being.
- Neglect of Responsibilities: Addiction often leads to neglect of important responsibilities, whether at home, work, or in parenting roles. This neglect can shift burdens onto partners or other family members, causing strain and resentment.
- Conflict and Abuse: Substance abuse can increase the likelihood of conflict and can escalate to verbal, emotional, or even physical abuse. The volatility associated with intoxication or withdrawal symptoms can create an unsafe environment for partners and children.
- Social Isolation: As addiction progresses, individuals may withdraw from social activities or neglect relationships with friends and extended family members. This isolation can weaken social support networks that are crucial for both the person with addiction and their close contacts.
- Codependency: Relationships where one partner has an addiction can lead to codependency, where the non-addicted partner may enable the addiction by covering up, supplying money, or taking on excessive caregiving responsibilities. This dynamic can hinder recovery and create an unhealthy balance in the relationship.
- Impact on Children: Parents with addiction may become emotionally distant or inconsistent, impacting their children’s emotional and psychological development. Children may take on caretaking roles prematurely, experience neglect, or develop anxiety and trust issues.
- Challenges in Recovery: Relationships can also be affected during the recovery process. Changes in dynamics, roles, and behaviors can be challenging for both the individual and their loved ones. Relationships may need to be reevaluated or rebuilt on new, healthier terms.
Addressing the impact of addiction on relationships often requires family therapy or couples counseling, in addition to individual treatment for addiction. These therapies can help repair and strengthen relationships, improve communication, and build a supportive environment conducive to recovery.
What Is The Impact of Drug Addiction on Society?
The impact of drug addiction is far-reaching, affecting the fabric of society at large, contributing to healthcare burdens, crime rates, strained social services, economic productivity loss, and other societal challenges. It is beyond just you or your loved ones and how you feel. Here’s how drug addiction affects the society.
- Increased Healthcare Costs: Drug addiction places a significant burden on healthcare systems. The costs associated with treating drug-related illnesses, overdoses, and infections like HIV and hepatitis can strain healthcare resources and lead to higher medical expenses for everyone.
- Crime and Violence: Drug addiction is often linked to criminal activities, including drug trafficking, theft, and violence. This can create unsafe communities, increase crime rates, and put additional pressure on law enforcement.
- Family Disruption: When a person battles drug addiction, their family members often experience emotional and financial stress. This can lead to family breakdowns, child welfare issues, and an increased need for social services.
- Workforce Productivity: Drug addiction can lead to decreased productivity and absenteeism in the workforce. This not only affects individual job performance but also has economic repercussions for businesses and the broader economy.
- The strain on Social Services: Substance abuse puts pressure on social services such as addiction treatment programs, emergency shelters, and welfare systems. Increased demand for these services can strain available resources and funding.
- Community Well-Being: Communities affected by high rates of drug addiction can experience a decline in overall well-being. This includes reduced property values, diminished quality of life, and a sense of insecurity.
- Stigmatization: People battling drug addiction often face social stigma and discrimination. This can hinder their ability to seek help, maintain relationships, and reintegrate into society.
- Cycle of Addiction: The societal impact of drug addiction can perpetuate a cycle, as children growing up in environments affected by addiction may be more vulnerable to substance abuse themselves.
What are the most extreme effects of drug addiction?
Drug addiction can have extreme and catastrophic impacts on individuals, particularly when it involves potent substances like Fentanyl, Xylazine, and Krokodile. Fentanyl, a synthetic opioid, is up to 100 times more potent than morphine and can lead to rapid respiratory failure, ultimately resulting in death. Xylazine, often used as a veterinary sedative, can cause severe respiratory depression and cardiac issues in humans. Krokodile, a homemade opioid, is notorious for its flesh-eating properties, leading to severe skin ulcers and infections that can necessitate limb amputation.
These extreme effects are not just isolated health incidents but ripple out to affect families, communities, and healthcare systems. The high potency and severe health ramifications of these drugs make them especially dangerous, often leading to rapid physical decline and posing significant challenges for emergency responders and medical professionals. The consequences of addiction to these substances are often irreversible, making awareness and prevention measures critically important.
What Are the statistics on the effects of drug abuse?
Drug abuse statistics underscore the serious and multifaceted impact of drug abuse on individuals, families, communities, and societies at large.
- Global Burden of Disease: According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, alcohol and drug abuse contribute significantly to the global burden of disease, with an estimated 11.8% of global disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) attributable to substance use disorders and their consequences. {PubMed}
- Impact on HIV: Injection drug use contributes to the spread of HIV/AIDS. Globally, an estimated 12% of new HIV infections are attributed to injection drug use and the sharing of contaminated needles. {CDC}
- Economic Costs: The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) estimates that drug abuse and its consequences cost societies worldwide hundreds of billions of dollars annually in healthcare expenses, lost productivity, and law enforcement efforts.
- Opioid Crisis: In the United States, the opioid epidemic has been particularly devastating. According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), in 2020, there were over 69,000 drug overdose deaths, with opioids, including prescription opioids, heroin, and synthetic opioids like fentanyl, being the primary drivers, an increase from opioid-related overdose in 2019..
- Youth and Substance Abuse: The Monitoring the Future survey found that while drug use among American teens has declined over the years, the use of certain substances, such as vaping products, marijuana, and prescription medications, remains a concern.
- Prison Population: The U.S. has a significant number of individuals incarcerated for drug-related offenses. According to the Bureau of Justice Statistics, in 2019, nearly 20% of federal and 15% of state prisoners were serving sentences for drug offenses.
- Treatment Gap: There is a significant treatment gap in the U.S., with many individuals in need of substance abuse treatment not receiving it. According to SAMHSA’s National Survey on Drug Use and Health, in 2020, only about 16% of people aged 12 or older who needed substance use treatment actually received it.
Who is Most Likely To Become Addicted?

It’s crucial to understand the risk factors of addiction and who’s most likely to become addicted. You must understand that addiction doesn’t discriminate, but certain factors can increase the risk of you or a loved one becoming prone to an addiction. It’s crucial to remember that addiction can happen to anyone, regardless of their background or circumstances, and it’s not a sign of weakness.
- Genetic Predisposition: If addiction runs in your family, you may have a higher risk due to genetic factors. This doesn’t mean you’re destined to become addicted, but it’s essential to be aware of your family history and take precautions.
- Early Exposure: Starting drug use at a young age, especially during adolescence when your brain is still developing, increases the risk of addiction. Your brain is more susceptible to changes that make addiction more likely.
- Mental Health Conditions: If you struggle with mental health issues like anxiety, depression, or trauma, you may be more vulnerable to addiction as drugs can provide temporary relief from emotional pain. It’s important to seek proper treatment for these conditions to reduce the risk.
- Peer Pressure and Environment: Being around people who use drugs or in an environment where drug use is prevalent can increase the likelihood of trying drugs. Peer pressure can be powerful, and it’s crucial to choose your social circle wisely.
- Availability and Accessibility: Easy access to drugs, whether through friends, family, or a neighborhood with high drug availability, can make it more likely for you to experiment and potentially become addicted.
- Stress and Life Challenges: Using drugs as a way to cope with stress, trauma, or difficult life events can lead to addiction. Developing healthy coping mechanisms is essential to reduce this risk.
- Lack of Education: Not having access to accurate information about the risks and consequences of drug use can make you more susceptible to addiction. Education and awareness play a significant role in prevention.
- Poverty and Socioeconomic Factors: Economic hardship, lack of access to quality healthcare, and limited opportunities can contribute to drug addiction. Addressing these socioeconomic factors is vital in reducing addiction rates.
- Personality Traits: Certain personality traits, like impulsivity and sensation-seeking behavior, can increase the risk of addiction. Recognizing these traits in yourself can help you make informed decisions.
Remember that addiction is a complex interplay of various factors, and it’s not your fault if you find yourself struggling with it. You’re not alone in this journey, and there’s hope for recovery and a healthier future.
How To Prevent Drug Addiction?

Substance use prevention is a difficult problem that governments and policymakers have tried to tackle for centuries. Here are the ways drug addiction can be prevented:
- Education: Start by learning about the risks and consequences of drug use. Understand how drugs affect your body and mind. Knowledge is a powerful tool for making informed decisions.
- Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Instead of turning to drugs when facing stress or difficult emotions, seek healthier ways to cope. This might include exercise, meditation, talking to a trusted friend, or pursuing creative outlets like art or music.
- Peer Pressure: Surround yourself with friends who support your well-being and make choices that align with your goals. Learn to say no to peer pressure, and don’t be afraid to distance yourself from people who encourage drug use.
- Mental Health: If you’re struggling with mental health issues, seek help from a therapist or counselor. Treating underlying mental health conditions reduces the risk of using drugs as a way to self-medicate.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Focus on maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular sleep, a balanced diet, and exercise. These factors can improve your resilience against addiction.
- Decriminalization: Certain states like Oregon have attempted to decriminalize drugs to bring down prison sentences for drug-related crimes and increase access to treatment.
A focus on preventing drug abuse is important because it addresses the problem before it occurs rather than after the fact with proactive measures to combat drug distribution and raise awareness.
What are the treatment options for drug addiction?

The treatment options for drug addiction can range from inpatient to outpatient treatment, group therapy, holistic treatment, and more. If you or a loved one are battling drug addiction, here’s what you can do.
- Seek Professional Help: Reach out to a healthcare professional or addiction counselor. They can assess your situation and recommend appropriate treatment options.
- Detoxification: In some cases, medical detox may be necessary to safely manage withdrawal symptoms. This should always be done under the supervision of medical experts.
- Therapy and Counseling: Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or motivational interviewing, can help you understand and change the thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to addiction.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups, like Narcotics Anonymous or SMART Recovery, provides a sense of community and understanding from others who have faced similar challenges.
- Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT): In certain situations, medications can be prescribed to help manage cravings and reduce the risk of relapse. MAT is often used for opioid and alcohol addiction.
- Lifestyle Changes: Make significant changes in your life to avoid triggers and situations that promote drug use. This may include changing your social circle or finding new, drug-free hobbies and interests.
- Long-Term Support: Recovery is an ongoing process. Stay engaged in your treatment plan and continue seeking support even after initial treatment. Many people find that long-term support is essential for maintaining sobriety.
Sources
Ben Fisher
All author postsShare This Post