Sober living facilities are crucial components in the continuum of addiction recovery care. They provide a structured and supportive environment essential for individuals transitioning from more intensive treatment phases to routine daily living without substance use. Established under the guidance of the National Association of Recovery Residences (NARR) in 2011, these facilities operate under a set framework designed to ensure safe, healthy, and substance-free living conditions.
A sober living facility is a type of residence that provides a supportive and drug-free environment for individuals recovering from addiction where peer recovery takes place under house guidelines. It is a place where people can live together with others who are also on the path to recovery. They emphasize mutual support and skills development necessary for sustained recovery and reintegration into the community.
In a sober living facility, residents are expected to maintain their sobriety and follow certain rules and guidelines like staying drug and alcohol-free, attending support group meetings, participating in house chores, and adhering to curfews.
What Are The Rules For Sober Living Homes (SLH’s)?
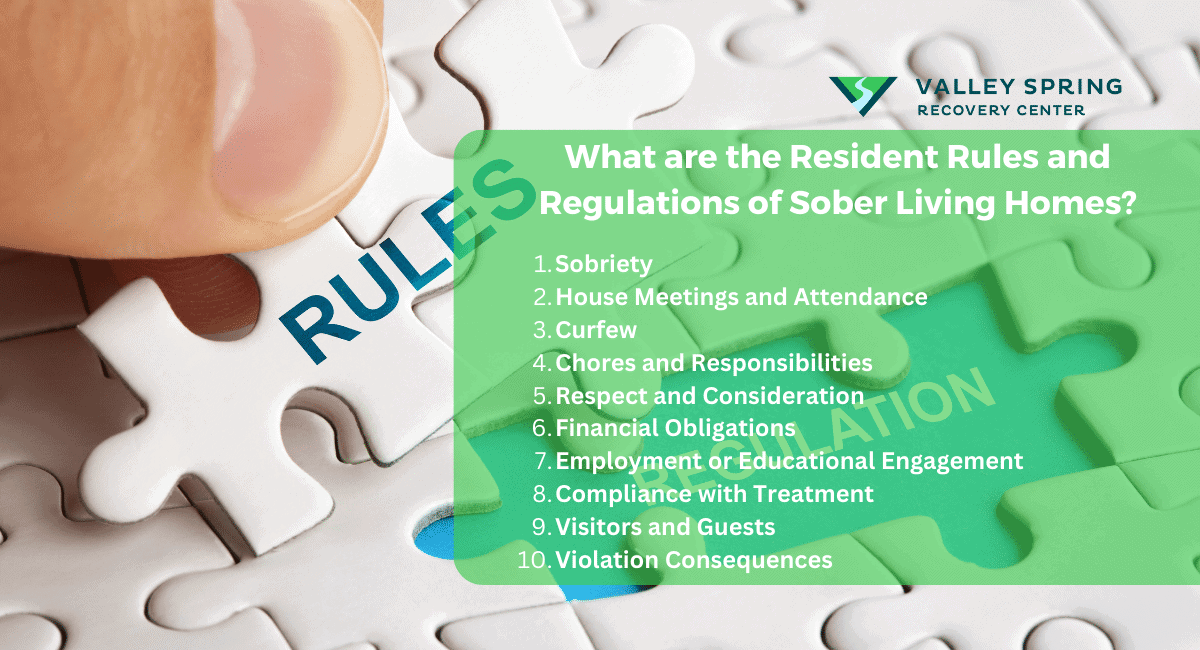
Resident rules and regulations in sober living homes range from a commitment to sobriety to a restriction on guests and visitors. While specific rules may vary among different sober living homes, here are some common rules and regulations that residents are typically expected to follow:
1. Sobriety
Maintaining sobriety is a fundamental rule in sober living homes. Residents are required to abstain from the use of alcohol and drugs. Regular drug testing may be conducted to ensure compliance.
2. House Meetings and Attendance
Residents are expected to attend house meetings, which provide an opportunity for open communication, support, and addressing any concerns or issues within the home. Attendance at these meetings is usually mandatory.
3. Curfew
Sober living homes often have a curfew in place to promote structure and accountability. Residents are expected to adhere to the designated curfew time and communicate any necessary exceptions or delays in advance.
4. Chores and Responsibilities
Residents are typically assigned household chores and responsibilities. These may include cleaning common areas, maintaining personal spaces, and contributing to the overall cleanliness and orderliness of the home.
5. Respect and Consideration
Residents are expected to treat fellow residents, staff, and visitors with respect, kindness, and consideration. This includes maintaining appropriate boundaries, refraining from disruptive behavior, and constructively resolving conflicts.
6. Financial Obligations
Residents are responsible for paying their rent and any other associated fees promptly. Financial contributions help cover the costs of operating the sober living home and maintaining its services and amenities.
7. Employment or Educational Engagement
Many sober living homes encourage residents to engage in employment, educational pursuits, or volunteer work. Residents are typically expected to actively seek employment or engage in activities that contribute to their personal growth and self-sufficiency.
8. Compliance with Treatment
Residents may be required to continue participating in outpatient treatment, counseling, or support group meetings as part of their recovery plan. Adherence to recommended treatment and therapy is typically expected.
9. Visitors and Guests
Each sober living home will have its own policy regarding visitors and guests. Residents are generally required to follow guidelines related to visitation hours, guest registration, and ensuring that visitors do not disrupt the recovery-focused atmosphere of the home.
10. Violation Consequences
Sober living homes have a system in place to address rule violations. Consequences for non-compliance may range from verbal warnings to probationary periods or, in more severe cases, termination of residency.
It is important to note that these rules and regulations are designed to create a supportive and accountable environment. They help foster personal growth, recovery, and the development of essential life skills.
What are the Resident Rules and Regulations of Sober Living Homes That Differentiate them from halfway houses?
The research by Polcin & Henderson in 2008 highlighted distinct characteristics that set sober living homes apart from halfway houses. Here’s a detailed look at these features:
- Alcohol and Drug-Free Environment: Sober living homes strictly enforce an environment free from alcohol and drugs. This foundational rule supports individuals in their commitment to abstain from substance use, providing a safe space conducive to recovery.
- Support Through 12-Step Programs: Unlike halfway houses that might offer a variety of formal treatment services, sober living homes typically do not provide formal treatment. Instead, they mandate or strongly encourage participation in 12-step self-help groups like Alcoholics Anonymous. This approach leverages peer support and a proven framework for sobriety.
- Structured Living Through House Rules: Residents must adhere to house rules, which include maintaining abstinence, paying rent and other associated fees, participating in house chores, and attending house meetings. These rules are designed to foster a sense of responsibility, discipline, and community among residents.
- Financial Responsibility: Residents are responsible for their own financial contributions towards rent and other living costs. This aspect of sober living promotes independence and accountability, preparing residents for life outside the supportive environment.
- Long-Term Residency Option: One significant feature of sober living homes is the flexibility in the length of stay. Residents can stay as long as they need, provided they adhere to the house rules. This contrasts with many halfway houses, which often have a set program duration.
These characteristics make sober living homes a unique and effective modality for individuals seeking to sustain their recovery in a supportive, communal living arrangement. This environment not only fosters sobriety but also aids in the gradual reintegration of individuals into broader society with a stronger foundation in their recovery journey.
Why Do Sober Living Homes Have Rules?
Sober living homes play a critical role in supporting recovery from substance abuse by providing a structured, supportive, and drug-free environment. The rules in these homes are designed not only to support individual recovery processes but also to ensure the safety and well-being of all residents. Here’s how these rules are established and why they are essential:
1. Support Recovery Process: Sober living homes are designed to offer residents a stable environment that minimizes the temptations and risks associated with early recovery stages. Rules help maintain a routine, promote discipline, and ensure that the home operates under a recovery-oriented ethos.
2. Ensure Resident Safety: Rules are in place to protect the health and safety of residents. This includes policies against substance use, curfews to maintain order, and protocols to handle emergencies or conflicts within the home.
3. Build Sober Lifestyles: By enforcing a structured lifestyle, these homes help residents develop habits and skills necessary for a sober life, such as accountability, responsibility, and self-care practices.
The core principles set by the National Association For Recovery Residences (NARR) are followed by individual standards that establish the minimum criteria for certification. Depending on the residence level, meeting each of the 31 standards across the 10 principles is required for certification.
The NARR Standard categorizes recovery-oriented housing into four levels of support, each with specific operational guidelines to suit varying degrees of resident independence and care needs. The standards were developed collaboratively by recovery housing experts, providers, and stakeholders across the nation to ensure they comprehensively address the needs of individuals in recovery.
What Are The Benefits of Sober Living Homes?
Sober living homes (SLHs) offer a structured and supportive environment that plays a crucial role in the recovery process for individuals recovering from substance abuse. The primary benefits documented by research, including a study led by Polcin et al. in 2010, emphasize the importance of a stable, drug-free living environment for sustaining abstinence:
- Stable Recovery Environment: SLHs provide a drug-free environment critical for individuals at various stages of recovery, particularly those transitioning from more intensive treatment settings. The stability and routine fostered in these homes help prevent relapse.
- Peer Support and Community: Living with others in recovery helps foster a supportive community where residents can share experiences and challenges. Polcin’s research highlights the positive impact of peer support found in SLHs, which is often facilitated through structured activities and shared responsibilities.
- 12-Step and Recovery Involvement: Most SLHs encourage or require participation in 12-step programs, which Polcin et al. found to be a strong predictor of positive outcomes. This structured approach to sobriety supports long-term recovery goals.
- Improved Employment and Psychiatric Symptoms: Residents often experience improved employment outcomes and reduced psychiatric symptoms, as SLHs provide a conducive environment for personal development and professional growth.
- Reduction in Criminal Behavior and Substance Use: The study noted a decrease in arrests and sustained reductions in substance use among residents, contributing to safer communities and better individual outcomes.
The Impact of Rules Based on NARR Standards are listed below:
- Administrative and Operational Standards: Ensure that sober living homes are well-managed and adhere to legal and ethical guidelines.
- Physical Environment Standards: Guarantee that the living environment is safe, clean, and conducive to recovery.
- Recovery Support Standards: Provide frameworks for the kind of peer support, recovery planning, and goal-setting that facilitate effective recovery.
- Good Neighbor Standards: Help residences operate in harmony within community settings, fostering good relationships with neighbors and local authorities.
These rules and standards are not just bureaucratic measures; they are vital for creating an environment that supports recovery. By fostering a sense of community, stability, and safety, these standards help residents focus on their recovery journey without the added stress of instability or unsafe conditions.
What Are the Risks and Downsides of Sober Living Homes?
While SLHs are beneficial, they also come with potential challenges and limitations which are listed below.
- Varying Levels of Structure and Support: The effectiveness of SLHs can vary widely depending on the management and the specific rules enforced. Less structured environments might not provide sufficient support for some residents.
- Cost Factors: The costs associated with living in SLHs might be prohibitive for some individuals. Although residents typically pay for their own costs, the financial burden can be significant.
- Limited Stay Duration: Some SLHs have policies that limit the duration of stay, which may not align with the individual needs of residents. Transitioning out before one is ready can pose a risk to their recovery.
- Dependency on Group Dynamics: The community-based model of SLHs means that individual recovery experiences can be heavily influenced by group dynamics. Negative interactions or relapses within the group can impact other residents.
- Relapse Risks: Despite the supportive environment, relapses can and do occur within SLHs. The presence of relapse can undermine the recovery process for others in the home.
- Regulatory and Funding Challenges: As noted by Polcin, SLHs often operate without formal regulation or government funding, making them vulnerable to operational challenges and inconsistencies in quality.
Sober living homes are a critical component of the recovery landscape, offering numerous benefits but also facing distinct challenges. For those considering this option, it’s important to weigh these factors carefully and choose a home that best meets individual recovery needs.
Who can Go to a Sober Living Home?
While specific criteria may vary among different sober living homes, here are some general groups of people who can benefit from residing in a sober living home:
1. Individuals Completing Addiction Treatment
Sober living homes often serve as a transitional step for individuals who have completed an addiction treatment program, such as inpatient rehabilitation or outpatient counseling. These homes provide a supportive environment that helps individuals maintain their sobriety and apply the skills they learned during treatment in a real-world setting.
2. Those Seeking a Structured and Supportive Environment
Sober living homes can be beneficial for individuals who recognize the need for a structured and accountable environment as they navigate early recovery. These homes offer a safe and supportive space where residents can receive peer support, guidance, and encouragement from fellow residents who are also on a similar recovery journey.
3. Individuals without a Stable Living Environment
Some people face challenges in maintaining a stable and drug-free living environment due to various factors, such as unstable housing, strained family relationships, or lack of a supportive network. Sober living homes provide a stable and substance-free residence, eliminating potential triggers and providing the necessary structure for individuals to focus on their recovery.
4. Those Seeking Continued Support and Accountability
Recovery from addiction is an ongoing process that requires ongoing support and accountability. Sober living homes offer a community of individuals with shared experiences and a commitment to sobriety. This peer support can be invaluable in maintaining long-term recovery and preventing relapse.
5. Individuals Transitioning from Incarceration
Sober living homes can also be a beneficial option for individuals transitioning from incarceration back into the community. These homes provide a structured and supportive environment to help individuals reintegrate into society, access necessary resources, and establish a stable foundation for successful reentry.
It is essential to note that sober living homes may have specific admission criteria, such as a commitment to sobriety, completion of a treatment program, or adherence to house rules.
Overall, sober living homes offer a supportive and accountable environment for individuals in various stages of recovery, helping them build a strong foundation for sustained sobriety and a healthier lifestyle.
Is there a specific treatment program completion requirement for residents?
The specific treatment program completion requirement for residents in sober living homes can vary depending on the facility. While some sober living homes may require residents to have completed a formal addiction treatment program, such as inpatient rehab or outpatient counseling, others may not have this specific requirement.
The purpose of requiring treatment program completion is to ensure that residents have received a foundational level of support, education, and skill development in their recovery journey before transitioning to a sober living home. Completing a treatment program provides individuals with the tools and coping strategies necessary to maintain sobriety and make progress in their recovery.
Can individuals with a criminal background join a sober living home?
Some sober living homes may have restrictions on accepting individuals with certain types of criminal backgrounds, particularly if there are concerns about the safety and well-being of other residents. This is done to maintain a secure and supportive environment within the sober living home.
However, it’s important to note that not all sober living homes have strict restrictions related to criminal backgrounds. Some homes may be more open and considerate, taking into account factors such as the nature of the offense, the individual’s commitment to recovery, and their willingness to abide by the rules and guidelines of the facility.
What are the consequences of violating the rules in a sober living home?
Consequences for violating rules in a sober living home can vary, but they typically aim to promote accountability and a supportive recovery environment. Residents may receive verbal warnings for minor infractions, while repeated or serious violations can lead to probation, mandatory counseling, or community service.
In more severe cases, suspension or discharge from the facility may occur. The consequences are designed to encourage personal growth, maintain a safe environment, and reinforce the importance of following the rules to support residents’ recovery journeys.
How do sober living homes and inpatient residential treatment programs compare in their effectiveness at creating supportive social environments that facilitate sustained recovery from substance abuse?
The effectiveness of both sober living homes and inpatient residential treatment programs in creating supportive social environments crucial for recovery from substance abuse has been a subject of significant research and development. Historically, the proliferation of inpatient and residential treatment programs in the 1960s and 1970s marked a critical shift in addressing substance abuse. These programs, as highlighted by White (1998), were designed to remove clients from destructive living environments that perpetuated substance use and to establish new, supportive social networks within treatment settings.
Inpatient residential treatment programs typically provide a structured and intensive treatment environment where clients live full-time, receiving constant medical care and therapy. This model is highly beneficial for individuals requiring a stable environment free from external triggers, thus significantly aiding in the initial stages of recovery.
On the other hand, sober living homes serve as a transitional housing option where individuals can live after completing a residential treatment program or while they are engaged in outpatient treatment. These homes do not typically provide clinical treatment but focus on fostering independence and responsibility in a supportive, drug-free environment. Research, including studies by Braucht et al. (1995), Hitchcock, Stainback, & Roque (1995), and others, have shown that halfway houses and sober living environments significantly improve treatment outcomes by extending the support network and allowing residents to practice sobriety in a less restrictive, yet supportive, environment.
Comparatively, while inpatient programs are essential for dealing with acute phases of addiction and providing immediate medical and psychological care, sober living homes excel in offering a longer-term support system that encourages personal growth and integration into society. Both play critical roles in the continuum of care for substance abuse recovery, each addressing different needs and stages of the recovery process. By leveraging the strengths of both environments, individuals have a better chance of achieving and maintaining sobriety.
Do sober living homes allow MAT?
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is recognized as an effective recovery tool when combined with supportive services, enhancing both engagement and outcomes for individuals in recovery from addiction. According to the National Alliance for Recovery Residences (NARR), MAT includes physician-prescribed medications that are part of a comprehensive treatment plan. There are important legal and operational guidelines that sober living homes must follow regarding MAT.
Sober living home operators cannot legally deny admission solely based on an individual’s use of prescribed MAT. However, these residents may choose not to accept individuals who require medications that they are not equipped to manage. In such cases, they should refer these individuals to facilities that can meet their needs.
Under recently updated NARR standards, certified sober living homes are encouraged to provide secure storage for medications and facilitate access to MAT as prescribed. These homes are also encouraged to maintain a supply of naloxone and ensure staff are trained in overdose reversal, supporting a safer recovery environment.
Sober living homes are allowed and, in some cases, required to accommodate residents who are prescribed MAT as part of their recovery process. These homes play a crucial role in supporting sustained recovery, provided they have the appropriate resources and policies in place to safely manage the specific needs of individuals on medication-assisted treatment.
How do regular sober living homes and luxury sober living homes differ in scope?
Sober living homes provide essential support to individuals recovering from addiction, offering a drug-free environment that promotes sobriety and personal responsibility. These homes vary significantly in scope and amenities, which can be broadly categorized into regular and luxury sober living homes. Each type serves the same fundamental purpose but differs in the level of comfort, amenities, and additional services offered.
2. Regular Sober Living Homes
Regular sober living homes are focused primarily on providing a safe and supportive environment for residents. These facilities typically offer basic amenities such as shared bedrooms, communal living spaces, and necessary household facilities. The emphasis is on creating a community-oriented atmosphere where residents participate in shared responsibilities like chores and attending group meetings. These homes are generally more affordable and emphasize peer support and self-sufficiency as crucial elements of recovery.
3. Luxury Sober Living Homes
Luxury sober living homes, on the other hand, offer a higher standard of living with enhanced amenities that can include private rooms, gourmet meals prepared by professional chefs, and beautifully landscaped grounds. These facilities often provide additional services such as on-site counseling, holistic therapies like yoga and meditation, personal training sessions, and recreational activities. The environment in luxury sober living homes is designed to provide maximum comfort and support to residents, which can be particularly appealing to those who are used to a higher standard of living or who may benefit from a more intensive level of care during their recovery.
Ben Fisher
All author postsShare This Post