Adderall Use and Anxiety: Does It Help?

Adderall is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant prescribed primarily for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), not anxiety disorders. This prescription medication functions by increasing the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which are neurotransmitters associated with attention, alertness, and executive function. According to the New Jersey Prescription Monitoring Program (2023), ADHD diagnoses in the state have risen by 32% over the past decade, intensifying interest in how stimulant medications like Adderall affect related psychological conditions, such as anxiety disorders.
There are three main types of Adderall: immediate-release (IR), extended-release (XR), and mixed amphetamine salts formulations. Although this ADHD medication may temporarily reduce anxiety in individuals with ADHD by improving task focus and reducing cognitive overload, Adderall is not an anxiolytic and may exacerbate anxiety in individuals without ADHD or those with comorbid anxiety disorders. The physiological stimulant effect, such as increased heart rate, heightened alertness, and disrupted sleep patterns, can mimic or intensify symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, or social anxiety disorder. These amphetamine-based medications can also trigger anxiety symptoms in people with pre-existing mental health conditions.
“It’s a common misconception that because Adderall improves focus, it will automatically reduce anxious feelings. In reality, it can make anxiety worse if misprescribed or taken without clinical supervision, but it can be helpful if someone is struggling with ADHD.” says Dr. Michael Olla, MD, a New Jersey-based psychiatrist specializing in addiction medicine.
To assess the drug’s efficiency and safety, clinicians employ validated psychometric tools such as the GAD-7 scale for anxiety and Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scales to differentiate overlapping symptoms. Effective treatment often requires multimodal interventions, such as combining behavioral therapy with the correct pharmacological agents.
What Is Adderall?
Adderall is a prescription stimulant used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It combines two active ingredients, amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which stimulate your brain’s central nervous system. The drug increases the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters responsible for regulating attention, alertness, and impulse control.
In New Jersey, Adderall remains one of the most frequently prescribed medications for ADHD. According to the New Jersey Prescription Monitoring Program (2023), stimulant prescriptions, including Adderall, accounted for over 1.2 million dispensed doses, with usage rates highest among individuals aged 18 to 34.
When you take Adderall, the drug activates areas in your brain like the prefrontal cortex, which governs decision-making, focus, and working memory. As a result, you feel more attentive, less impulsive, and mentally organized.
Adderall is usually prescribed in two forms: immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (XR), with dosage personalized based on your medical condition and response to treatment.
Did you know most health insurance plans cover substance use disorder treatment? Check your coverage online now.
Does Adderall Help With Anxiety?
As a stimulant medication, Adderall increases levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which are neurotransmitters associated with focus and alertness, but these same brain chemicals also intensify the physiological arousal linked to anxiety disorders. According to a 2020 study published in Neuropsychopharmacology, stimulant medications can elevate heart rate, blood pressure, and cortisol levels, which are biological markers commonly heightened during anxiety episodes and panic attacks.
There are two primary types of anxiety: state anxiety (temporary and situational) and trait anxiety (long-term and persistent). Adderall may worsen both, particularly trait anxiety, by chronically eleThere are two primary types of anxiety: state anxiety (temporary and situational) and trait anxiety (long-term and persistent). Adderall may worsen both anxiety types, particularly trait anxiety, by chronically elevating neural excitation and disrupting homeostatic balance in the limbic system. This amphetamine-based medication can trigger fight-or-flight responses in individuals prone to anxiety symptoms.vating neural excitation and disrupting homeostatic balance in the limbic system.
From a pharmacodynamic standpoint, Adderall’s mechanism of action directly conflicts with the therapeutic goals of anxiolytic medications, such as SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) or benzodiazepines, which aim to reduce excessive brain stimulation. While Adderall may indirectly reduce perceived anxiety in individuals with ADHD by improving executive functioning and reducing task-related stress, this effect is secondary and not consistent across patient populations. The medication’s stimulating properties can create anxiety-like symptoms even in people without pre-existing anxiety disorders.
To measure the impact of Adderall on anxiety symptoms, clinicians typically rely on standardized tools such as the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7). Clinical outcomes generally show an increase, not a decrease, in anxiety scores among patients without ADHD or those with comorbid anxiety disorders.
Why Do Some People Feel Calmer On Adderall?
Some people feel calmer on Adderall because the drug increases mental clarity and control in those with ADHD. For these individuals, their baseline brain activity is under-stimulated. Adderall balances their dopamine and norepinephrine levels, helping them feel focused, organized, and emotionally regulated.
This calming effect is not universal and reflects how Adderall affects neurochemical imbalances in ADHD, not anxiety itself. For someone without ADHD, this feeling is mistaken for calmness when it’s actually hyperfocus or emotional flattening. That distinction is critical.
Using Adderall without a clinical diagnosis quickly leads to psychological dependence. You begin to rely on it for everyday functioning, not just symptom control. Repeated use increases the risk of tolerance, which pushes you toward higher doses and addiction. This cycle opens the door to addiction.
Can Adderall Make Anxiety Worse?
Yes, Adderall makes anxiety worse for many people, especially if you already have an anxiety disorder. As a stimulant, it raises activity in your central nervous system. This leads to physical symptoms like restlessness, rapid heartbeat, muscle tightness, and racing thoughts. These responses mimic or intensify the sensations you already feel during an anxiety episode.
The drug also elevates stress hormones like cortisol and activates your brain’s fight-or-flight response. Over time, this keeps your body in a state of alertness. If you live with anxiety, that stimulation feels overwhelming instead of helpful. You focus better, but your emotional regulation suffers. This imbalance leads to panic, irritability, and disturbed sleep.
Contact us today to schedule an initial assessment or to learn more about our services. Whether you are seeking intensive outpatient care or simply need guidance on your drug addiction journey, we are here to help.
What’s The Difference Between ADHD And Anxiety Symptoms?
The difference between ADHD and anxiety symptoms is rooted in intention and origin. ADHD affects how you initiate and sustain attention. Anxiety affects how you process threats and stress. While both cause restlessness, poor focus, and irritability, the causes and directions of these symptoms differ.
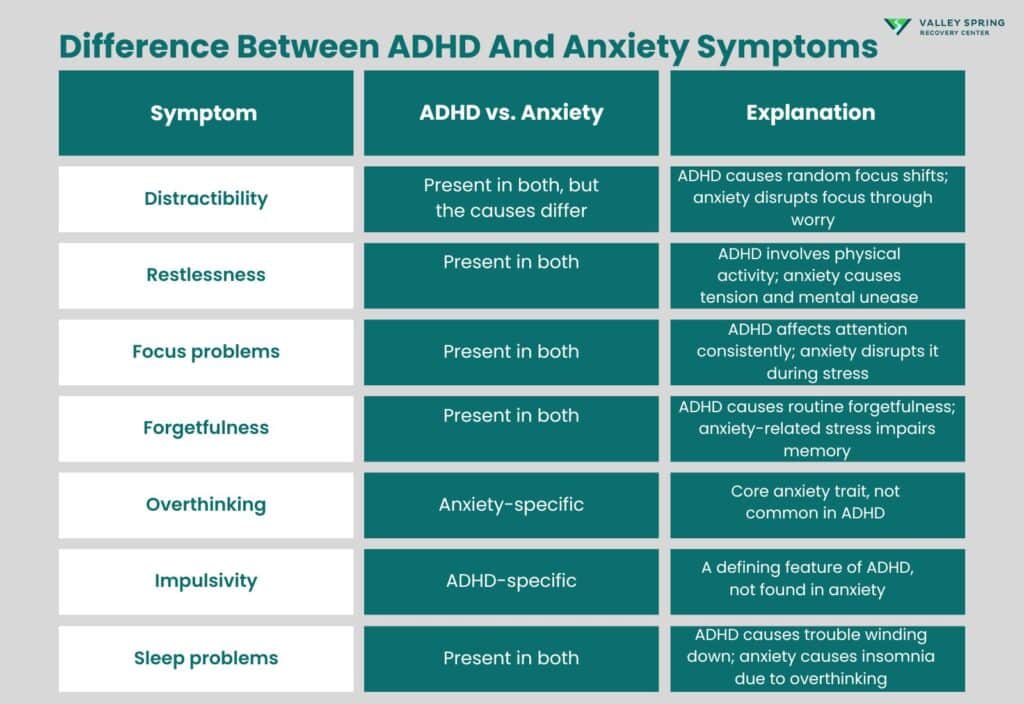
The table below shows the difference between ADHD and anxiety symptoms:
| Symptom | ADHD vs. Anxiety | Explanation |
| Distractibility | Present in both, but the causes differ | ADHD causes random focus shifts; anxiety disrupts focus through worry |
| Restlessness | Present in both | ADHD involves physical activity; anxiety causes tension and mental unease |
| Focus problems | Present in both | ADHD affects attention consistently; anxiety disrupts it during stress |
| Forgetfulness | Present in both | ADHD causes routine forgetfulness; anxiety-related stress impairs memory |
| Overthinking | Anxiety-specific | Core anxiety trait, not common in ADHD |
| Impulsivity | ADHD-specific | A defining feature of ADHD, not found in anxiety |
| Sleep problems | Present in both | ADHD causes trouble winding down; anxiety causes insomnia due to overthinking |
Is It Dangerous To Take Adderall If You Have Anxiety?
Yes, it is dangerous to take Adderall if you have anxiety without medical supervision. The stimulant effect of Adderall increases nervous system activity, which intensifies your anxiety symptoms. You experience a faster heart rate, increased blood pressure, jitteriness, and emotional discomfort.
These physical effects overlap with anxiety, making symptoms worse instead of better. Adderall interacts poorly with unmanaged anxiety. You might feel more reactive, restless, or overwhelmed. For people with Generalized Anxiety Disorder or Panic Disorder, stimulant exposure triggers episodes or escalates chronic worry into panic attacks.
Long-term use of Adderall also increases the risk of psychological dependence. If you’re using the drug to “feel normal” or to suppress stress without treating the anxiety directly, the risk of addiction rises. You build tolerance, leading to dose escalation, and dependency develops as your brain adapts to artificial stimulation.
What Medications Are Actually Used To Treat Anxiety?
The medications used to treat anxiety are SSRIs, SNRIs, Benzodiazepines, Buspirone, and Beta-blockers. These drugs work differently from stimulants like Adderall and focus on lowering central nervous system arousal rather than increasing it.

The medications used to treat anxiety are:
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): SSRIs increase serotonin in your brain, which stabilizes mood. Common examples include sertraline (Zoloft) and escitalopram (Lexapro).
- Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): SNRIs raise both serotonin and norepinephrine levels, helping reduce anxiety and physical tension. Venlafaxine (Effexor XR) and duloxetine (Cymbalta) are common options.
- Benzodiazepines: These drugs offer fast relief by slowing brain activity. Used short-term due to addiction risk. Alprazolam (Xanax) and lorazepam (Ativan) are common.
- Buspirone: A non-addictive anti-anxiety medication that works gradually by adjusting serotonin receptors.
- Beta-blockers: prescribed for social anxiety or performance anxiety, these control physical symptoms like rapid heart rate. Propranolol is an example.
If you’re using Adderall without a prescription or to manage stress, it’s important to understand that anxiety responds to a different class of medication. If misuse has already started, speak to a professional about an Adderall rehab program to safely reset your treatment path.
Rediscover Life at Valley Spring Recovery Center
Get the compassionate support you deserve. We're here to help you reclaim joy, wellness, and a brighter future.
Verify Benefits
Can You Take Adderall And Anxiety Medication Together?
Yes, you can take Adderall and anxiety medication together, but only under strict medical supervision. This combination is sometimes used for people diagnosed with both ADHD and anxiety disorders. The treatment must be balanced carefully because stimulants like Adderall increase nervous system activity while many anxiety medications work to slow it down.
The risk increases when these medications interact unpredictably. For example, combining Adderall with benzodiazepines blunts the stimulant’s effects, while SSRIs alter how your body processes Adderall, potentially intensifying side effects like insomnia or irritability. Doctors monitor dosage, timing, and symptom patterns closely to avoid dependency, emotional instability, or worsened anxiety.
How Do Doctors Treat Patients With Both ADHD And Anxiety?
Doctors treat patients with ADHD and anxiety by using a layered approach that targets both conditions without worsening either. The first step involves identifying which condition is more impairing. If anxiety is severe, treatment usually begins with an SSRI or therapy before introducing a stimulant like Adderall. If ADHD symptoms are dominant, low-dose stimulant treatment is introduced first while monitoring anxiety levels closely.
In dual-diagnosis cases, treatment plans are adjusted based on how your brain responds to medication combinations. Doctors recommend non-stimulant ADHD medications like atomoxetine or extended-release stimulants that reduce anxiety-related spikes.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is also used alongside medication to help you manage both thought patterns and behavior. This dual-diagnosis strategy reduces symptom overlap and helps maintain emotional stability while improving attention and daily function.
What Should You Do If Adderall Is Increasing Your Anxiety?
What you should do if Adderall is increasing your anxiety includes speaking to your doctor, avoiding changing the dose yourself, and asking about alternatives. These actions reduce risk and help you safely manage both ADHD and anxiety without worsening either condition.

What you should do if Adderall is increasing your anxiety is explained below:
- Contact your healthcare provider immediately: Explain the anxiety symptoms in detail, including when they began. Your provider evaluates whether Adderall is the right fit for your condition. Timely reporting helps prevent worsening symptoms.
- Do not self-adjust the dosage: Changing your dose without guidance disrupts your treatment. It increases the risk of withdrawal and side effects. Always follow a doctor’s plan when modifying stimulant use.
- Ask about alternative medications: Non-stimulant ADHD options and targeted anxiety treatments exist. These reduce conflict between symptoms. Your doctor tailors a safer combination for your needs.
Share This Post













