Driving under the influence (DUI) poses a serious risk to public safety, and New Jersey is no exception. The state faces significant consequences from DUI incidents. An annual report from the State Police highlights that intoxicated drivers are now the leading cause of all fatal crashes in New Jersey, surpassing distracted driving for the first time in a decade. To illustrate the substance abuse issue further, statistics from the New Jersey Substance Abuse Monitoring System (NJ-SAMS) for the calendar year 2019 provide insight into the substances most frequently involved. Alcohol remains the predominant factor in these DUI cases, which also comprises 41% of rehabilitation admissions with 958 alcohol related admissions. cases.
These statistics underline the critical nature of DUI as a threat to road safety. By understanding the extent and specifics of DUI-related incidents, New Jersey residents and authorities can take appropriate measures to enhance vigilance and safety on the roads.
DUI Incidents and Statistics in New Jersey
Despite having one of the lowest rates of DUI fatalities, New Jersey experienced a 30% increase in DUI incidents and crashes in 2021, with significant contributions from drug intoxication, particularly cannabis, affecting not only drivers but also pedestrians and cyclists.
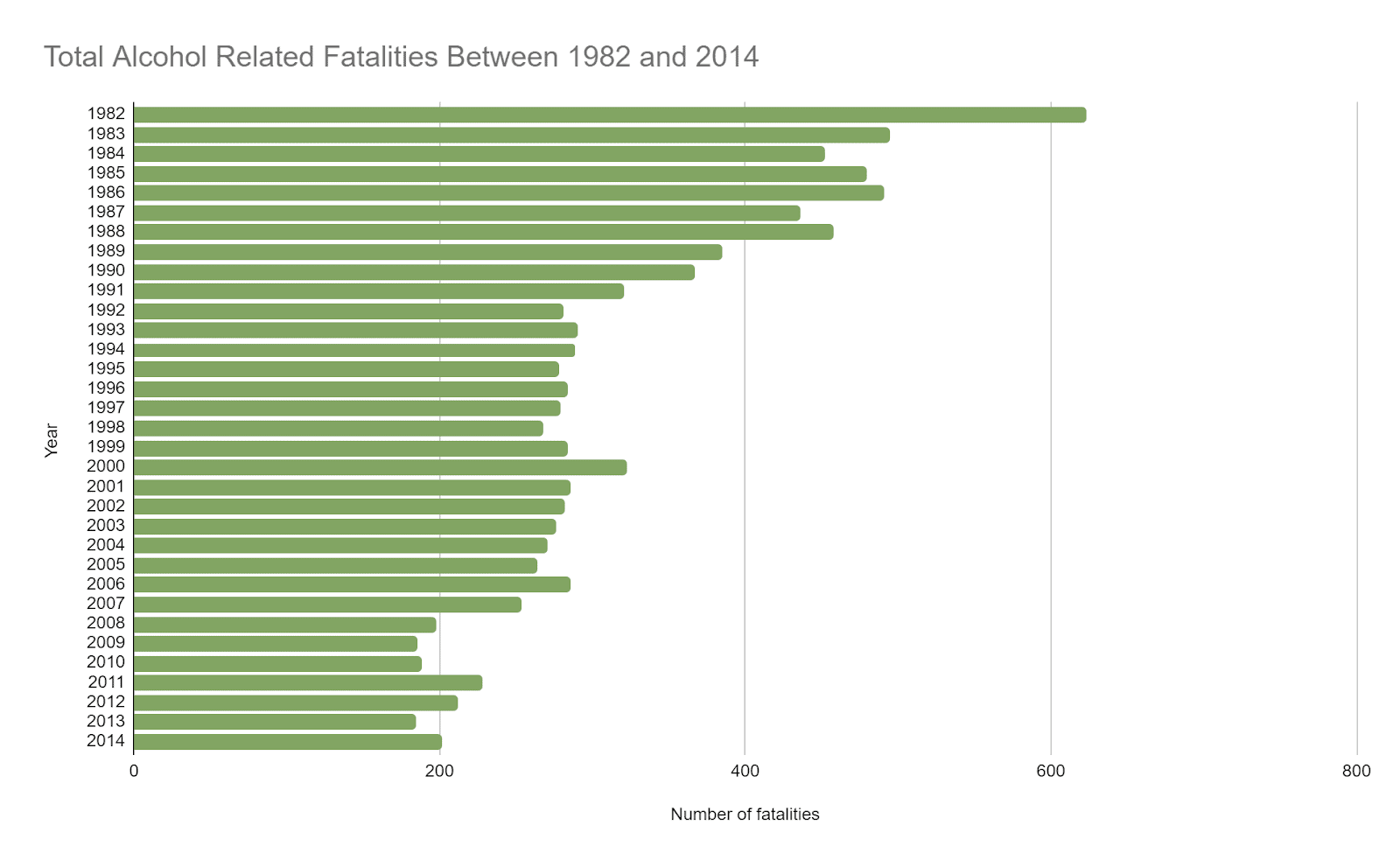
- In 2021, a total of 697 people met their deaths in 667 crashes. Out of this, drug intoxication was responsible for 210 fatal crashes, resulting in the death of 228 people.
- There has been a staggering 30% increase in DUI incidents and crashes from the year 2020 when there were a total of 162 crashes. These numbers have been increasing for the third time in a row, and even COVID-19 did not affect these rising rates.
- Further investigation revealed that 91 drivers of the 210 were intoxicated by cannabis. In addition, 23 pedestrians, 13 passengers, and 2 cyclists were also under the influence of the same drug.
- The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that a total of 1459 people were killed by alcohol-impaired drivers between the years 2008 and 2019.
- Men are 2x as likely to die than women when involved in alcohol-related incidents.
- The 2017 New Jersey State Police Report concluded that over 25% of the 5316 motorcycle-related deaths deaths were a result of blood alcohol content being over the legal limit of 0.08%.
- The Office of the Attorney General stated alcohol impairment is about four times at night when compared to daytime, and close to 30% of the fatal crashes that occur are due to alcohol intoxication.
The most concerning aspect is that there are no proper metrics or protocols to determine what limit of drug intoxication is acceptable and not acceptable, unlike alcohol intoxication, which a simple breath test can determine.
Additionally, there is no solid research to determine the extent to which these drugs can alter human perception and contribute to crashes. At the same time, all the data is available in the case of alcohol intoxication.
The figure below illustrates the percentage of fatalities that occur at various times of the week as per the 2021 NHTSA reports.
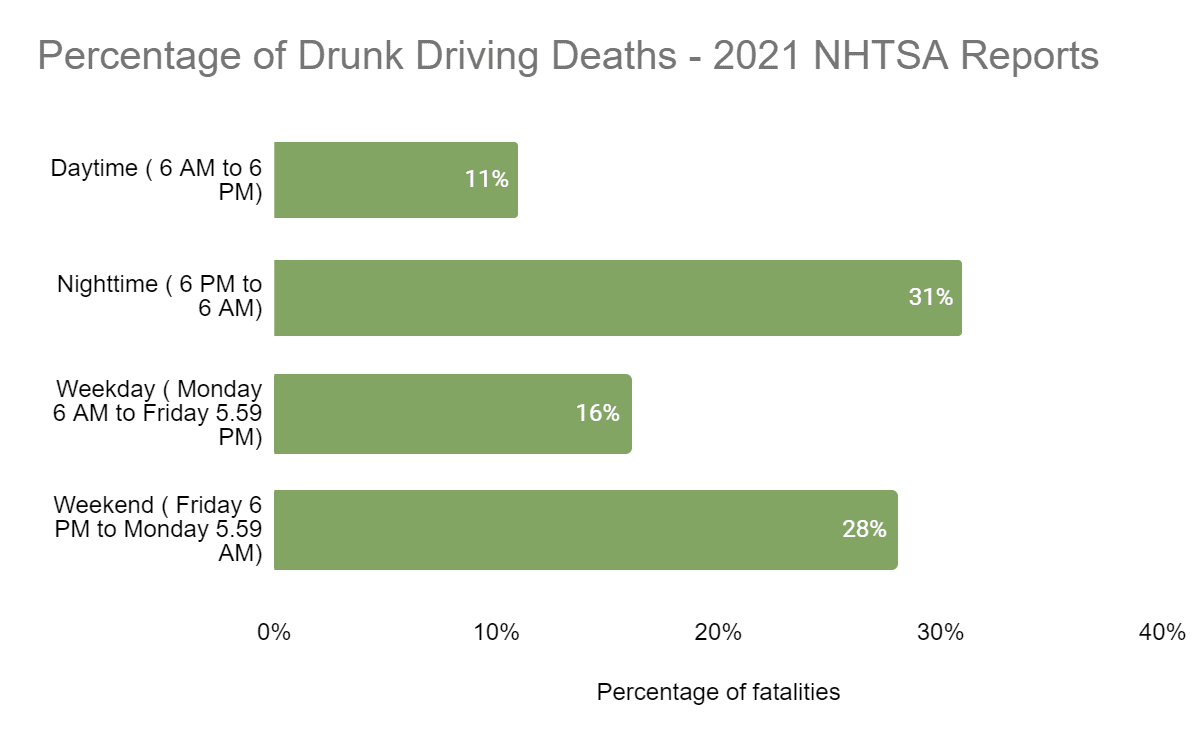
The statistics and trends of the state of New Jersey align with these statements.
This means that the deadliest times are Friday and Saturday evenings and nights. Therefore, citizens on the road need to be extra cautious on weekends.
Various sources have also concluded that most of these accidents are caused by people in their 20s or between 50 and 64. Additionally, state and county roads are reportedly the most accident-prone zones, as per the same reports.
As many as 443,000 people were arrested on suspicion of DUI in the year 2021, as per the FBI data, and about 11.2% of these arrests took place in New Jersey alone.
What Are The DUI Causes and Impacts?
DUI causes and impacts stem largely from drivers underestimating the risks of driving while impaired. Repeated instances of DUI can lead drivers to falsely believe it’s harmless, ignoring how alcohol and drugs significantly impair physical and motor skills, as well as the brain’s decision-making capabilities. Even minimal alcohol consumption can profoundly affect one’s ability to perceive and react, increasing the risk of fatal accidents. Furthermore, DUI carries not only the cost of human lives—including drivers, passengers, pedestrians, and cyclists—but also imposes a substantial financial burden, costing taxpayers approximately $992 million annually. This financial strain underscores the broader societal impacts of DUI, beyond individual tragedies.
Strategies to Reduce DUI Cases
While the number of DUI cases can not be immediately reduced to zero, implementing the strategies below might help reduce the number of DUI cases over time.
- Lowering the Blood Alcohol Concentration Limit
The current BAC limit in New Jersey is set at 0.08 g/dL; therefore, further reducing this limit to 0.05 g/dL can be a significant step towards securing roads.
The CDC reported that Utah implemented this limit in 2018, which resulted in an 18% reduction in the total crash death rate per mile!
- Increased Taxation and Restrictions
Alcohol and drugs come under the class of demerit goods, which harm people if misused. Therefore, the government needs to take measures to make these substances less accessible to citizens.
This can be done by imposing regulations on the concentration of alcohol shops in a region or limiting the amount of alcohol sold to an individual. In fact, the Jersey State Assembly’s ministers initially had proposed an 8.9% increase in Alcohol duty for 2024 but later fixed it at 4.5%, with 27 ministers in favor, 19 against the motion, and 1 abstaining.
In addition, increased taxation on these products will also ensure that people are discouraged from consuming them in large quantities. Strict regulations should also be imposed on pharmaceutical shops to only provide drugs like painkillers in limited amounts as prescribed by medical experts.
- Spreading Awareness
We discussed earlier how people become complacent when avoiding accidents or mishaps, even when driving under the influence. This is precisely why awareness programs should be curated, and various media, such as social media and print media, can proliferate awareness about the dangers of driving under the influence.
The statistics and figures should be highlighted to create a more significant impact. In addition, children also need to be taught in schools about the consequences of driving under the influence. Instilling this knowledge from a young age will ensure that children become responsible adults.
- The Pedestrians Challenge
To further reduce fatal accidents due to intoxication, it is paramount that pedestrians are also made aware of the dangers of being on the road under the influence. Alcohol and other drugs often affect the stability of the body. Therefore, people must be accompanied by someone sober or ensure they are not walking too close to the road.
This is because all it takes is a loss of balance for a few seconds before a grave accident occurs. Therefore, it is not just the people who drive that need to take precautions; it is also the people who are walking on the streets.
Our admissions department is available 24/7 and happy to answer any questions you may have about our facility or treatment options.
What Are The Laws and Consequences for NJ DUIs?
New Jersey enforces strict DUI laws to address and deter driving under the influence of alcohol and drugs. The consequences for DUI offenses vary based on the severity of the incident, the driver’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) at the time of arrest, and prior offenses. Here is a breakdown of the legal repercussions for various types of DUI offenses in New Jersey:
For Alcohol-Related DUI with BAC of 0.10% or Greater, or Drug-Related DUI:
- License Suspension: 7 months to 1 year
- Fines and Surcharges: $300 to $500 fine, plus additional fees including a $230 Intoxicated Driver Resource Center (IDRC) fee, $100 to the drunk driving fund, $100 to the Alcohol Education and Rehabilitation Fund (AERF), and a $1,000 annual surcharge for three years.
- Prison Term: Up to 30 days
- Other Penalties: Mandatory 12-48 hours in the IDRC and installation of an ignition interlock device during the license suspension and for 6 months to 1 year following license restoration for those with a BAC of 0.15% or greater.
For Alcohol-Related DUI with BAC between 0.08% and less than 0.10%:
- License Suspension: 3 months
- Fines and Surcharges: $250 to $400 fine, plus additional fees including a $230 IDRC fee, $100 to the drunk driving fund, $100 to AERF, and a $1,000 annual surcharge for three years.
- Prison Term: Up to 30 days
- Other Penalties: Mandatory 12-48 hours in the IDRC.
For Repeated DUI Convictions:
- Second Offense within 10 Years:
- License Suspension: 2 years
- Fines and Surcharges: $500 to $1,000 fine, plus additional fees similar to the first offense.
- Prison Term: 48 hours to 90 days
- Other Penalties: Mandatory 30 days of community service, 12-48 hours in the IDRC, and an ignition interlock device during the suspension and for 1-3 years following restoration.
- Third Offense within 10 Years of the Second:
- License Suspension: 10 years
- Fines and Surcharges: $1,000 fine, with increased surcharges including a $1,500 annual surcharge for three years.
- Prison Term: 180 days
- Other Penalties: Up to 90 days of community service (which can reduce the prison term), mandatory 12-48 hours in the IDRC, and an ignition interlock device during the suspension and for 1-3 years following restoration.
Related Offenses:
- Driving or Riding with an Open Container:
- First Offense: $200 fine.
- Second Offense: $250 fine and 10 days of community service.
- Driving with a DUI Suspension: Additional license suspension for 1-2 years, $500 fine, $250 annual surcharge for three years, and a prison term of 10-90 days. In certain cases, this can be an indictable offense with up to 180 days in jail.
- Driving While Possessing Drugs:
- License Loss: 2 years
- Fines: Minimum $50 fine.
These laws and penalties reflect New Jersey’s commitment to reducing DUI-related incidents and enhancing road safety. They serve as a deterrent and a reminder of the serious consequences of driving under the influence.
What is the legal blood alcohol concentration (BAC) limit in New Jersey?
New Jersey drug and alcohol laws state the legal blood alcohol concentration (BAC) limit is 0.08 grams per deciliter (g/dL) for most drivers. For commercial drivers, the limit is set at 0.04 g/dL, and for drivers under the age of 21, any detectable amount of alcohol can lead to a DUI charge as part of the state’s zero-tolerance policy.
Our admissions department is available 24/7 and happy to answer any questions you may have about our facility or treatment options.
How does alcohol affect driving ability?
Alcohol impairs several essential driving skills, including reaction time, coordination, concentration, and judgment. Even small amounts can affect driving ability, with increased risk for accidents as BAC levels rise. At a BAC of 0.08%, muscle coordination becomes poor, and the ability to detect danger decreases, significantly impairing driving skills.
What are the BAC limits for a DUI in New Jersey?
Penalties for a DUI in New Jersey vary depending on the number of offenses and the driver’s BAC level. For a first offense with a BAC of 0.08% but less than 0.10%, penalties may include a fine, a license suspension for three months, and up to 30 days in jail. Higher BAC levels and subsequent offenses result in more severe penalties, including longer jail times, larger fines, and extended license suspensions.
Can a DUI charge affect employment in New Jersey?
Yes, a DUI charge can significantly impact employment, especially if the job involves driving. Employers may have policies that restrict hiring individuals with DUI convictions, and commercial drivers may lose their licenses, directly impacting their employment status.
What are the long-term effects of a DUI on a person’s life?
The long-term effects of a DUI can include increased insurance costs, job difficulties, and financial strain due to legal fees and fines. Additionally, a DUI conviction may lead to a criminal record, which can affect future employment opportunities, educational prospects, and personal relationships.
How can DUI crashes be prevented?
Preventing DUI crashes involves a combination of law enforcement, public education, and personal responsibility. Effective strategies include sobriety checkpoints, strict enforcement of DUI laws, public awareness campaigns about the dangers of drunk driving, and promoting the use of designated drivers or alternative transportation options like taxis and ridesharing services.
What role does law enforcement play in preventing DUIs?
Law enforcement officers play a crucial role in DUI prevention through patrols, checkpoints, and the strict enforcement of laws regarding driving under the influence. These activities increase the perceived risk of arrest, which can deter individuals from drunk driving.
How effective are public awareness campaigns in reducing DUI incidents?
Public awareness campaigns are effective in educating the public about the risks associated with drunk driving and can change harmful behaviors. Campaigns that use a combination of emotional appeals and factual information about the consequences of DUI tend to be the most effective.
What alternatives are there to driving under the influence?
Alternatives to driving under the influence include using public transportation, calling a taxi or ridesharing service, arranging for a designated driver, or staying overnight at a friend’s home. Planning ahead when drinking can help avoid the need to make decisions about driving while impaired.
How can someone help a friend who frequently drives under the influence?
Helping a friend who frequently drives under the influence involves addressing the behavior directly and expressing concern for their safety and the safety of others. Offering to be a designated driver, suggesting alternative transportation options, or encouraging participation in programs designed to help with alcohol misuse can also be effective. If the behavior continues, it may be necessary to involve other friends, family members, or seek professional help.
What is the extent of the drug and alcohol abuse problem in New Jersey?
New Jersey faces significant challenges with drug and alcohol abuse, mirroring national trends but with some unique local characteristics. The state has been particularly impacted by the opioid epidemic, with a high number of opioid-related overdoses and deaths. According to the New Jersey Department of Health, there were over 3,000 suspected drug-related deaths in 2020, with a large proportion involving opioids. Alcohol abuse also remains a persistent issue, contributing to numerous health problems and fatalities. The CDC reports that excessive drinking is responsible for one in ten deaths among working-age adults, and the implications in New Jersey addiction statistics align with these findings. The state continues to implement various programs and initiatives aimed at combating these pervasive problems, focusing on treatment, prevention, and education to reduce the incidence of substance abuse and its associated impacts.
Do mental health statistics correlate with DUI and drunk driving?
Mental health statistics do correlate with DUI and drunk driving. Research has consistently shown that individuals with mental health disorders are more likely to engage in substance use, including alcohol, which can lead to impaired driving and increased DUI incidents. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder can lead to self-medication with alcohol, thereby increasing the risk of DUI if individuals choose to drive while under the influence.
Furthermore, studies have indicated that substance abuse, including alcohol misuse, is often comorbid with mental health disorders. For example, the National Institute on Mental Health (NIMH) reports that about one-third of people experiencing mental illnesses and about half of people living with severe mental illnesses also experience substance abuse. This dual diagnosis can complicate treatment and increase the risk of dangerous behaviors such as drunk driving.
Addressing mental health substance use disorder effectively can potentially reduce DUI rates, as better mental health support and treatment can decrease the likelihood of substance use as a coping mechanism. Therefore, integrating mental health services with substance abuse treatment programs (dual diagnosis treatment programs) is crucial in reducing DUI incidents and supporting the overall well-being of individuals.
Ben Fisher
All author postsShare This Post