Addiction, an insidious and pervasive societal challenge, extends its reach far beyond the individual caught in its grip, affecting entire families and relationships. According to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), 46.3 million people aged 12 or older (or 16.5 percent of the population of the U.S.) met the applicable DSM-5 criteria for having a substance use disorder in 2020, including 29.5 million people who were classified as having an alcohol use disorder and 24 million people who were classified as having a drug use disorder, underscoring the alarming prevalence of this issue (SAMHSA, 2021).
Addiction is a chronic and compulsive dependence on substances or behaviors by one family member that disrupts the harmony, trust, and emotional well-being within sibling relationships. It often involves the persistent use of substances like drugs or alcohol, leading to adverse consequences not only for the addicted individual but also causing ripple effects that reverberate through the family unit.
Siblings of addicts may experience emotional distress, strained communication, and a sense of instability as they navigate the challenges presented by their brother’s or sister’s addictive behavior. The dynamics of addiction in this context encompass not only the individual struggles of the addicted sibling but also the broader impact on the familial bonds and the well-being of all involved.
Strategies siblings can use to provide support and mend relationships with the addicted family member include open communication, education and awareness, and the establishment of healthy boundaries.
How Are Siblings of Addicts Affected by Substance Abuse?
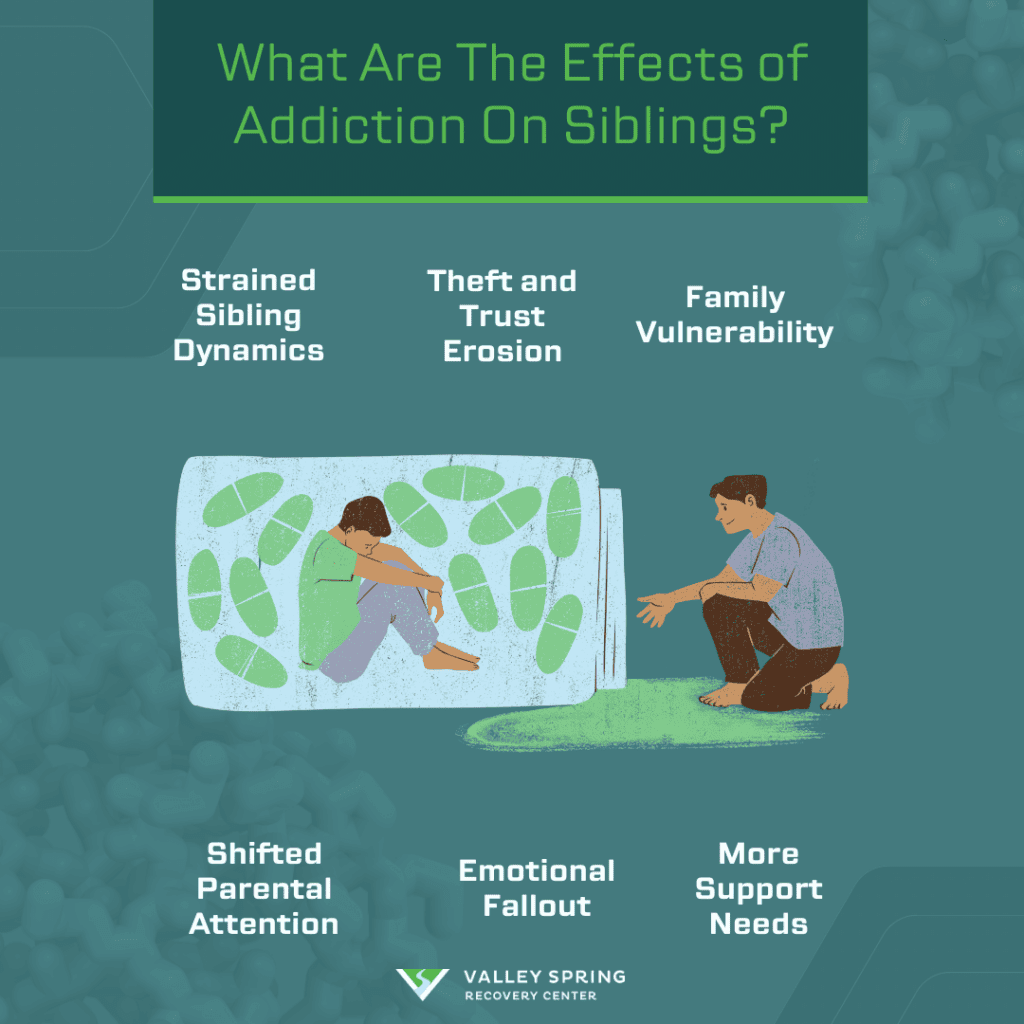
Substance abuse within a family significantly strains sibling dynamics, leading to emotional neglect, trust issues, financial strain, and long-term impacts on mental health and personal development which are highlighted in the 2020 research study by Prudence Mafa and Jabulani Calvin Makhubele.
- Strained Sibling Dynamics: Aggressive behavior, communication breakdowns, and financial demands from an addicted sibling create tension and disrupt family bonds.
- Shifted Parental Attention: Parents focusing on the addicted sibling can lead to emotional neglect of others, stirring resentment and weakening sibling relationships.
- Theft and Trust Issues: Addicted siblings may steal from family members, eroding trust and causing financial and emotional strain.
- Emotional Turmoil: Threats, intimidation, and potential violence from an addicted sibling foster an environment of unease and vulnerability.
- Increased Caretaking Roles: Non-addicted siblings may assume caretaker responsibilities, leading to premature stress and responsibility.
- Social Isolation: Stigma associated with addiction can cause siblings to withdraw socially, feeling judged or embarrassed.
- Mental Health Impact: The stress and chaos of dealing with addiction can lead to anxiety, depression, and other psychological issues for siblings.
- Disrupted Development: The focus on an addicted sibling’s needs can interrupt personal growth and aspirations of others.
- Altered Family Roles: Siblings may take on untraditional roles within the family hierarchy, affecting dynamics and relationships.
- Guilt and Responsibility: Siblings might feel guilty for not preventing the addiction or believe they are somehow responsible.
- Exposure to Substance Use: Close proximity to substance abuse can increase the risk of other siblings experimenting with or developing addictions.
- Compromised Family Resources: Addiction strains family finances, limiting resources for education, activities, and personal growth for siblings.
- Legacy of Addiction: The long-term impact of addiction can influence siblings’ views on substance use, trust, and family dynamics.
- Relationship Challenges: Trust issues and emotional scars from dealing with an addicted sibling can hinder healthy relationships outside the family.
How can siblings protect their mental health while dealing with a brother or sister’s addiction?
Siblings can protect their mental health by setting emotional boundaries, seeking personal therapy or support groups, and prioritizing self-care activities to manage stress and maintain emotional balance.
What steps can parents take to ensure all their children feel supported when one child is battling addiction?
Parents can ensure all children feel supported by providing equal attention, recognizing each child’s individual needs, facilitating open family discussions, and encouraging participation in family therapy sessions.
How can siblings rebuild trust after it’s been broken due to addiction-related behaviors like theft?
Rebuilding trust involves open communication, setting clear boundaries, and the addicted sibling taking responsibility for their actions through consistent behavior change and possibly restitution for past wrongs.
What are effective communication strategies for siblings and families affected by addiction?
Effective communication strategies include active listening, expressing thoughts and feelings without blame, using “I” statements, and engaging in mediated conversations with the help of a therapist if necessary.
How can families navigate the financial strain caused by a sibling’s addiction without compromising their own financial security?
Families can navigate financial strain by creating a budget that prioritizes essential expenses, seeking financial counseling, and exploring community resources designed to assist families impacted by addiction.
What resources are available for siblings looking to understand and cope with the emotional impact of addiction in the family?
Resources for siblings include support groups like Al-Anon or Nar-Anon, counseling services, online forums, and educational materials on addiction and family dynamics from reputable health organizations.
How can siblings maintain a healthy relationship with an addicted brother or sister without enabling their behavior?
Maintaining a healthy relationship involves expressing love and support for the sibling’s well-being while refusing to participate in or cover up behaviors that contribute to their addiction.
What are signs that siblings might need their own support or therapy to deal with the effects of addiction in the family?
Signs include feeling overwhelmed, experiencing anxiety or depression, struggling with feelings of guilt or anger, and having difficulty managing daily life or relationships due to the family situation.
How can siblings of addicted individuals prepare for potential relapses in their brother or sister’s recovery journey?
Preparation for potential relapses includes educating themselves about the recovery process, discussing relapse prevention plans with their sibling, and knowing how to respond in a supportive yet boundary-respecting manner.
What can siblings do to support their own futures and personal development while a family member struggles with addiction?
Siblings can focus on their personal development by setting goals, pursuing interests and education, seeking personal counseling to process their experiences, and building a supportive network outside the family.
How to help an addicted Sibling Without Enabling Further Substance Abuse?
Supporting an addicted sibling financially without inadvertently enabling their substance abuse requires careful consideration and a balanced approach. Here are some strategies to help when dealing with an addicted brother or sister:
- Direct Assistance for Basic Needs: Instead of giving cash, consider providing direct assistance for essential needs such as groceries, rent, or utilities. This ensures that your support contributes to their well-being rather than facilitating substance abuse.
- Gift Cards for Necessities: Provide gift cards for grocery stores, gas stations, or other essential services. This way, you can support their basic needs without giving them unrestricted access to cash.
- Direct Payment to Service Providers: Make payments directly to service providers, such as landlords or utility companies, rather than giving money to your sibling. This helps ensure that the funds are used for necessary expenses.
- Offering Non-Monetary Support: Instead of financial assistance, provide support in non-monetary ways. This could involve helping them find job opportunities, assisting with resume building, or providing emotional support during their recovery journey.
- Connect with Treatment Resources: Encourage your sibling to seek professional help for their substance abuse. Offer to assist in finding treatment programs, support groups, or counseling services that can address the root causes of their addiction.
- Set Boundaries: Communicate your willingness to support their recovery but establish boundaries regarding financial assistance. Let them know that your support is contingent on their commitment to addressing their substance abuse issues.
- Involve a Trusted Third Party: If appropriate, consider involving a trusted third party, such as a counselor, social worker, or addiction specialist, to help manage financial support. This ensures a more structured approach that aligns with your sibling’s recovery plan.
- Educate Yourself on Addiction: Gain a better understanding of addiction and recovery processes. This knowledge can help you provide informed and supportive assistance while avoiding actions that might unintentionally enable their substance abuse.
- Encourage Responsibility: Support your sibling in taking responsibility for their actions and decisions. Encourage them to engage in activities that promote personal growth and accountability, which are crucial aspects of the recovery process.
- Join a Family Support Group: Consider joining a family support group where you can share experiences and gain insights from others who have faced similar challenges. These groups provide valuable guidance on supporting loved ones without enabling destructive behaviors.
| Strategy | Description | How It Helps/Supports Addiction Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Assistance for Basic Needs | Provide direct help for essentials like groceries, rent, or utilities instead of giving cash, ensuring support aids well-being and not substance abuse. | Ensures basic living needs are met without enabling drug purchases. |
| Gift Cards for Necessities | Offer gift cards for essential services, supporting basic needs without enabling access to cash. | Limits the use of funds to necessities, reducing the risk of funding substance abuse. |
| Direct Payment to Service Providers | Pay landlords or utility companies directly to ensure funds are used for necessary expenses. | Guarantees that essential bills are paid, maintaining stability during recovery. |
| Offering Non-Monetary Support | Provide non-financial assistance such as job search help, resume building, or emotional support during recovery. | Enhances self-sufficiency and emotional well-being, critical for recovery. |
| Connect with Treatment Resources | Encourage and assist in finding treatment programs, support groups, or counseling to address addiction’s root causes. | Facilitates access to professional help, addressing underlying issues of addiction. |
| Set Boundaries | Communicate support for recovery with clear financial boundaries, contingent on their commitment to sobriety. | Reinforces the importance of responsibility and accountability in recovery. |
| Involve a Trusted Third Party | Involve professionals like counselors to manage financial support, ensuring alignment with the recovery plan. | Adds a layer of accountability and ensures financial support is used appropriately. |
| Educate Yourself on Addiction | Gain knowledge on addiction and recovery to offer informed support and avoid enabling substance abuse. | Empowers you to provide more effective support and avoid enabling behaviors. |
| Encourage Responsibility | Support your sibling in taking responsibility for their actions and decisions, promoting personal growth and accountability. | Limits the use of funds for necessities, reducing the risk of funding substance abuse. |
| Join a Family Support Group | Engage in groups for families facing similar issues for shared experiences and insights on non-enabling support. | Offers emotional support and practical advice, helping families navigate recovery together. |
How Do I Set Boundaries With My Addicted Sibling?
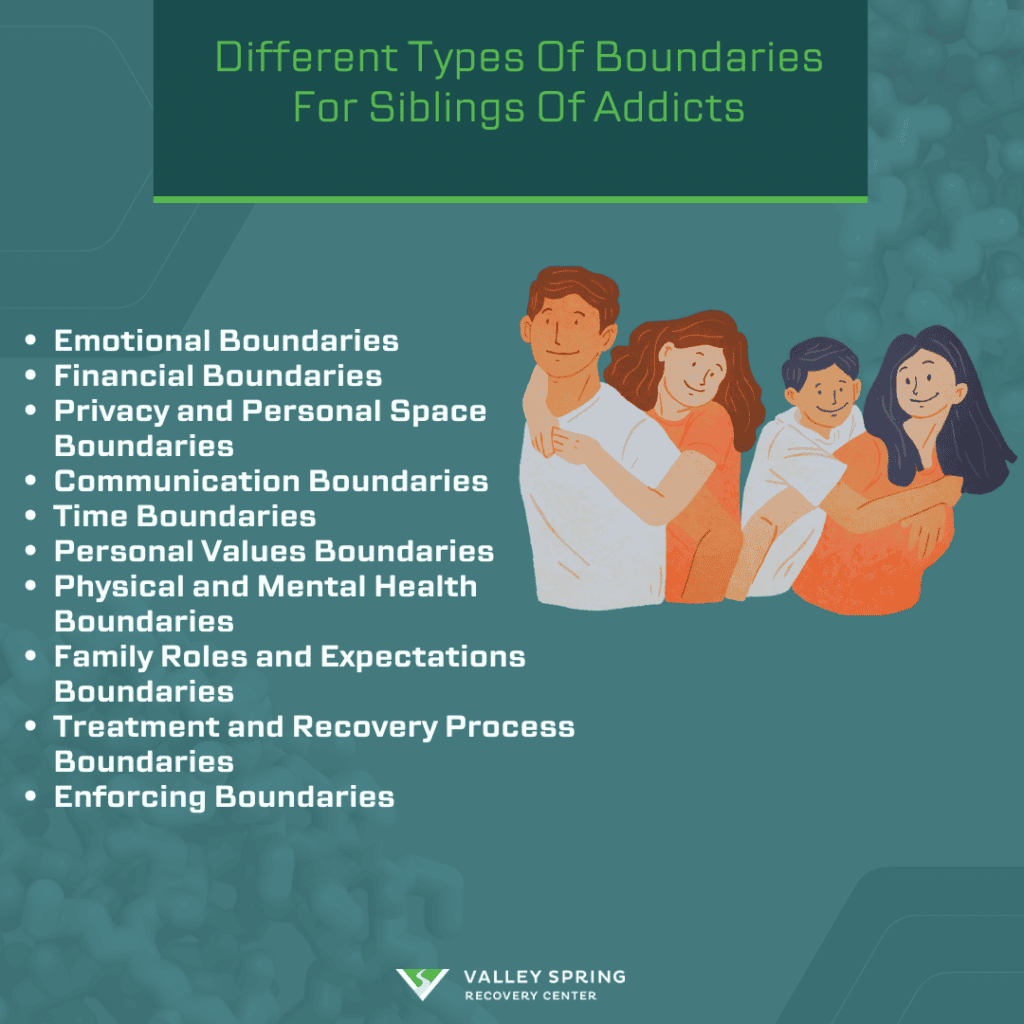
Boundaries for siblings of an addict refer to the clear lines or rules established to maintain a healthy relationship and personal well-being while supporting the sibling’s journey to recovery. These boundaries are crucial for defining acceptable behaviors, responsibilities, and limits on the assistance provided, ensuring that support does not enable addiction. They help protect the sibling from emotional or financial harm and encourage the addicted sibling to take responsibility for their actions and recovery process.
Setting boundaries with your addicted sibling is essential for both their well-being and your own, but it can be emotionally challenging. Start by clearly communicating your limits with empathy and love. Let them know that your decision is motivated by a desire for their recovery and your mental health. Understand that saying “no” doesn’t make you unsupportive; it establishes a necessary framework for accountability and peace of mind. Seek guidance from support groups or a therapist to reinforce your conviction in maintaining healthy boundaries, ultimately contributing to a more stable and supportive environment for your sibling’s recovery.
Here are 10 practical strategies siblings can employ when dealing with an addicted brother or sister:
- Education: To better cope with addicted siblings, education on the nature of addiction can be effective as well as learning the various treatment options.
- Set Boundaries: Siblings should establish clear boundaries, defining tolerated behaviors and consequences if those boundaries are crossed. For instance, sibblings may choose not to provide financial or emotional support during active substance use.
- Seek Professional Help: Dealing with an addicted sibling can be overwhelming, and seeking guidance from a therapist or counselor specializing in addiction and family dynamics is essential.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with other siblings facing similar challenges in support groups offers a sense of community, understanding, and encouragement.
- Take Care of Yourself: Siblings must prioritize their well-being, maintain a healthy lifestyle, engage in enjoyable activities, and seek support from their network.
- Focus on the Things You Can Control: Recognizing the limits of control over their sibling’s actions, siblings should concentrate on their behavior, choices, and well-being.
- Avoid Enabling Behavior: Steering clear of enabling actions, such as providing money or covering up for their sibling, is crucial for fostering healthy boundaries.
- Encourage Treatment: Siblings should encourage their addicted sibling to seek treatment, offering support in finding appropriate options and assisting in following through with treatment plans.
- Be Patient: Acknowledging the challenges of addiction recovery, siblings need patience, understand setbacks may occur, and should continue offering support throughout the process.
- Seek Help for Yourself If Needed: If the situation becomes emotionally distressing, siblings should not hesitate to seek professional help, ensuring they receive guidance and coping strategies to manage their stress.
How Do I Encourage Responsibility for My Sibling Without Neglecting?
Encouraging responsibility in your sibling without neglecting them involves finding a delicate balance between support and accountability. Communicate openly and non-judgmentally about your concerns and expectations, emphasizing your desire to see them thrive. Offer assistance in setting achievable goals and creating a plan for personal growth. Be a source of encouragement, acknowledging their efforts and progress while gently holding them accountable for their actions. Stay involved in their life, providing emotional support and guidance, but avoid enabling destructive behaviors. Strive for a supportive dynamic that fosters responsibility without neglecting their need for understanding and assistance during challenging times.
What are emotional boundaries, and how can they protect the well-being of a sibling not struggling with addiction?
Emotional boundaries help protect an individual’s mental health by limiting exposure to the addicted sibling’s harmful behaviors. They involve expressing feelings respectfully and seeking external support when needed, promoting a healthier dynamic.
Emotional boundaries can prevent emotional drain and burnout, preserving the sibling’s mental well-being.
Without these boundaries, one might become overly involved emotionally, leading to stress and potential mental health issues.
How do financial boundaries prevent enabling an addicted sibling while still offering support?
Setting financial boundaries involves offering support in ways that don’t directly finance the addiction, like paying for groceries instead of giving cash. This approach supports the sibling’s basic needs while discouraging substance abuse. It reduces the risk of funds being misused, encouraging responsible spending. Lack of financial boundaries may inadvertently fund the addiction, hindering recovery.
What are the boundaries related to personal space and privacy when living with an addicted sibling?
Maintaining personal space and privacy ensures a healthy living environment, allowing both siblings to have areas where they can retreat and rejuvenate, crucial for emotional well-being during recovery efforts.
Personal space boundaries provide a necessary respite for self-care and without them, the constant stress can lead to resentment and personal distress.
Can setting boundaries in communication help in managing relationships with a sibling dealing with addiction? If so, how?
Clear communication boundaries include honest conversations about acceptable topics and behaviors, helping to reduce conflicts and misunderstandings, and supporting a positive relationship through the recovery process.
Communication boundaries foster a respectful and supportive dialogue. Without such boundaries, interactions may become harmful or counterproductive to recovery.
What role do time boundaries play in supporting a sibling’s recovery without compromising one’s own responsibilities and needs?
Time boundaries ensure that supporting a sibling’s recovery does not overshadow personal responsibilities and self-care, helping to maintain a balanced life. If enforced, they help in managing one’s life effectively while still offering support. Without them, one may neglect personal obligations or self-care, leading to burnout.
How do boundaries regarding personal values influence the support offered to an addicted sibling?
Upholding personal values without compromise helps guide the support offered, ensuring actions align with moral beliefs, which is essential for both siblings’ integrity and well-being. If enforced, it maintains the supporter’s integrity and models healthy behavior. Ignoring these boundaries can lead to ethical dilemmas and personal regret.
What are the boundaries for physical and mental health that should not be compromised when dealing with a sibling’s addiction?
Protecting physical and mental health by not engaging in enabling behaviors and seeking personal therapy or support groups is crucial for the well-being of siblings not struggling with addiction. Enforcing these boundaries safeguards the caregiver’s health. Neglecting them can lead to physical exhaustion and mental health decline.
How can setting boundaries in family roles and expectations support the recovery of an addicted sibling?
Clarifying roles and expectations within the family can prevent the non-addicted sibling from assuming too much responsibility for the addicted sibling’s actions, promoting a healthier family dynamic. If enforced, this ensures a balanced family environment. Without clear boundaries, one might bear undue responsibility, causing stress and family tension.
What boundaries should be set regarding involvement in the addicted sibling’s treatment and recovery process?
Setting boundaries around involvement in treatment might include supporting from a distance and encouraging professional help without trying to manage the sibling’s recovery process personally. If enforced, it empowers the addicted sibling to take responsibility for their recovery. Over-involvement might hinder the development of autonomy in recovery.
How to enforce boundaries if an addicted sibling repeatedly disrespects them?
Enforcing boundaries requires consistency and may involve seeking external help or implementing consequences if boundaries are repeatedly disrespected, crucial for maintaining respect and safety within the relationship. Consistently reinforcing the importance of respect and accountability. Failure to enforce can lead to boundary erosion, diminishing the effectiveness of the support provided.
How Do I Rebuild The Trust I Lost With My Addicted Sibling?
Rebuilding trust with an addicted sibling is a delicate process that requires consistency, open communication, and genuine effort. Begin by acknowledging the past breaches and taking responsibility for your actions. Demonstrate a commitment to change through consistent and reliable behavior, ensuring that your words align with your actions. Foster open communication by actively listening to their concerns and feelings without judgment. Be patient; rebuilding trust is a gradual process, and allow your actions to speak louder than words. Offering ongoing support in their journey towards recovery can also contribute to rebuilding the foundation of trust between you and your sibling.
What Are The Treatment Options Available for an Addicted Sibling?
Addressing substance use disorders requires a comprehensive approach, and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) offers valuable insights into effective treatment options suitable for individuals of any age. From behavioral approaches empowering individuals to therapeutic communities promoting holistic lifestyles, SAMHSA’s guidelines span a spectrum of interventions.
Behavioral approaches to recovery include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Teaches anticipation of problems and coping strategies and monitors distorted thinking triggering substance use.
- Community Reinforcement Approach: Replaces influences leading to substance use with those reinforcing abstinence, addressing problem-solving and coping skills.
- Contingency Management (CM): Provides incentives for treatment participation, goal achievement, and avoiding substance use, promoting retention in treatment.
- Motivational Enhancement Therapy: Reduces ambivalence about treatment or stopping substance use, building a plan for change through motivational interviewing.
- Brief Strategic Family Therapy: Originates from the idea that negative behaviors stem from unhealthy family interactions, aiming to change interaction patterns.
- Family Behavior Therapy: Combines behavioral contracts with contingency management to address behavioral issues and substance use involving the individual and family.
- Functional Family Therapy: Engages the entire family in the treatment process, modifying family members’ behavior through communication and problem-solving techniques.
- Multidimensional Family Therapy: Combines family- and community-based treatment to foster family competency and collaborate with other systems.
- Therapeutic Communities: Involves an intensive treatment model promoting a holistic lifestyle, addressing social, psychological, and emotional behaviors leading to substance use.
- Medication for Substance Use Disorder: Medications are dispensed in various treatment settings, including outpatient and inpatient programs.
- Detoxification: Generally refers to a 3- to 5-day inpatient program with intensive medical monitoring and management of withdrawal symptoms. Detox is needed in cases where withdrawal symptoms are associated with life-threatening substances or due to psychosocial circumstances.
These treatment options offer a comprehensive approach to addressing substance use disorders in individuals, acknowledging diverse therapeutic modalities and support services suitable for people of any age.
How Do I Convince My Sibling to Go Into Rehab Without Forcing Them?
Convincing your sibling to consider rehab involves approaching the conversation with empathy and understanding rather than coercion. Begin by expressing your genuine concern for their well-being, emphasizing your love and desire to see them healthy. Share specific instances that illustrate the impact of their addiction on their life and relationships. Present drug and alcohol rehab as a supportive and transformative opportunity rather than a punitive measure. Offer information on the potential benefits, such as professional guidance, a supportive environment, and the tools for long-term recovery. Encourage an open dialogue, allowing them to express their feelings and concerns, and emphasize that the decision is ultimately theirs, highlighting your willingness to support them on their journey to recovery.
What Will Co-workers think if my sibling goes to rehab?
When a sibling goes to rehab, co-workers’ reactions can vary based on their personal beliefs, experiences with substance abuse, and understanding of addiction as a medical condition. However, several common perceptions and concerns might arise:
- Concern and Sympathy: Many co-workers may express concern and sympathy for your situation. They might understand that dealing with a family member’s addiction can be challenging and emotionally draining.
- Respect for Seeking Help: Some co-workers might view the decision to seek rehab positively, recognizing it as a courageous step towards recovery and health. There’s a growing awareness that addiction is a health issue that requires professional intervention.
- Curiosity or Intrusiveness: There may be co-workers who show curiosity and ask questions, some of which might feel intrusive. This can stem from a lack of understanding about addiction and rehab processes or mere curiosity about your personal life.
- Privacy Concerns: Concerns about privacy and gossip can arise, especially if the workplace environment is not conducive to confidentiality. You may want to consider how much information you are comfortable sharing.
- Support and Understanding: You may find that co-workers offer support and understanding, especially if they have had similar experiences in their own lives or with their family members.
- Misunderstanding and Stigma: Unfortunately, stigma around addiction still exists. Some co-workers might have misconceptions or judgmental attitudes towards those who undergo rehab, often due to a lack of understanding of addiction as a disorder.
- Impact on Professional Perception: If your sibling’s situation becomes widely known, there might be concerns about how it reflects on your professional image. While this is becoming less of an issue in many understanding and progressive work environments, it can still be a concern in some workplaces.
Navigating the Situation:
- Control the Narrative: You have control over how much you disclose about your sibling’s situation. Sharing information is entirely at your discretion.
- Seek Support: If you feel comfortable, confiding in a trusted co-worker or supervisor can provide a source of support and understanding.
- Professional Boundaries: Maintaining professional boundaries is crucial. You can acknowledge the situation without going into detail, especially if you are uncomfortable.
- Educate if Necessary: If you encounter misconceptions, and you feel comfortable doing so, gently educating co-workers about addiction as a medical condition can be helpful.
Remember, every workplace is different, and reactions can vary widely based on the culture of the organization and the individual attitudes of co-workers. Prioritizing your well-being and that of your sibling is paramount.
Ben Fisher
All author postsShare This Post