Mental Health Screening Tests, Types and Effectiveness
A mental health screening test is a tool that helps detect emotional or psychological concerns at an early stage. A screening test takes the form of a short questionnaire or digital self-assessment that measures sadness, worry, or stress. Mental health has become a major concern in New Jersey. About 27.7 percent of adults report anxiety or depression. This number highlights the importance of timely screenings for people of all ages.
Different types of mental health screening tests focus on specific conditions. For example, clinicians use the PHQ-9 for depression and the GAD-7 for anxiety. Schools, clinics, and online platforms provide these screenings for easy access. The effectiveness of mental health tests lies in their ability to guide early intervention. Mental health screening tests are not final diagnoses. They are effective first steps. Clinicians encourage individuals to seek professional evaluation after screening. This ensures that proper care and treatment follow.
What Are Mental Health Screening Tests?
Mental health screening tests are simple tools that help identify conditions like depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder. Screening tests include short questionnaires or checklists that guide individuals toward further evaluation. The main goal of mental health screening is early detection, which enables timely help and treatment.
Screenings are available online and in clinics. This availability makes them accessible to many people. Screenings give useful insights into mental health and encourage people to seek support when needed. These screenings act as a first step that connects unrecognized symptoms with proper care and support.
To illustrate their practical application and accessibility, consider the following examples:
- Primary Care: Doctors use tools like the PHQ-9 during check-ups to screen for depression.
- Schools/Universities: Digital screenings help students identify mental health needs privately.
- Workplace Programs: Employers provide confidential online tests to support employee wellness.
- Public Campaigns: Free online screenings raise awareness and promote early help-seeking.
Why Are Mental Health Screening Tests Important?
Mental health screening tests are important because they detect problems early and make timely support possible. Mental illness tests help uncover hidden symptoms and reduce the risk of conditions getting worse. These tests guide people toward professional care and empower them to act on their mental health needs. As a first step to recovery, mental screening plays a key role in improving both individual well-being and public health.
Here are some reasons why mental health screening is important;
Early detection of mental health issues
Early detection through screenings helps spot concerns before they escalate into serious conditions. This proactive step shortens the duration of illness. It also reduces the overall impact and improves long-term outcomes.
Facilitates timely intervention and support
Identifying conditions early allows individuals to access help when it is most effective. Timely support not only improves recovery but also lowers the risk of complications and healthcare costs.
Helps in planning targeted treatment strategies
Mental health screenings provide useful insights into a person’s mental health. These insights allow healthcare providers to design tailored treatment plans. Personalized strategies improve effectiveness, increase engagement, and support better recovery results.
What Are the Types of Mental Health Screening Tests?
The types of mental health screening tests include the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7), Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A), Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ), Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS), PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5), and Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT). These tools are designed to screen for specific conditions such as depression, anxiety, ADHD, PTSD, and substance use. These mental health screening tools are not diagnostic on their own. They provide a valuable first step toward identifying concerns. Mental illness tests also encourage people to seek professional support.
Here is a detailed breakdown of some common tests, how they are conducted, and what individuals might experience during the process:
| Test Type | Target Disorder | Conduct Method | Typical Questions/Assessments | Experience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) | Depression | Self-administered questionnaire | Questions about mood, pessimism, sense of failure, self-dissatisfaction, guilt, punishment feelings, suicidal thoughts, crying, agitation, loss of interest, indecisiveness, worthlessness, loss of energy, changes in sleeping pattern, irritability, changes in appetite, concentration difficulty, tiredness or fatigue, loss of interest in sex | Individuals rate their feelings over the past week, including today, on a scale of 0-3 for each category. |
| Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) | Depression | Self-administered or clinician-guided questionnaire | 9 items based on the DSM-IV depression criteria such as little interest or pleasure in doing things, feeling down, trouble sleeping, feeling tired, poor appetite or overeating, feeling bad about yourself, trouble concentrating, moving or speaking slowly or too fast, thoughts of hurting yourself | Individuals reflect on the frequency of these issues over the past two weeks. |
| Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7) | Anxiety | Self-administered questionnaire | 7 items assessing symptoms of anxiety such as feeling nervous, not being able to stop or control worrying, worrying too much about different things, trouble relaxing, being so restless that it’s hard to sit still, becoming easily annoyed or irritable, feeling afraid as if something awful might happen | Responses are based on the frequency of these symptoms over the last two weeks. |
| Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) | Anxiety | Clinician-administered interview | 14 items including anxious mood, tension, fears, insomnia, cognitive, somatic (muscular, sensory, cardiovascular, respiratory, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, autonomic, behavior at interview) | The clinician rates the severity of each symptom based on the interview, observations, and patient’s report. |
| Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) | Bipolar Disorder | Self-administered questionnaire | Questions focus on symptoms of mania or hypomania, such as periods of elevated mood, increased activity or energy, risky behavior, spending sprees, hypersexuality, racing thoughts, less need for sleep | Individuals answer yes or no to experiencing symptoms, and if yes, whether these occurred at the same time, causing significant problems. |
| Adult ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS) | ADHD | Self-administered questionnaire | 18 items based on the DSM-IV criteria for ADHD, covering inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity symptoms such as making careless mistakes, difficulty keeping attention, not following through on instructions, difficulty organizing tasks, losing things necessary for tasks, being easily distracted, forgetfulness in daily activities, fidgeting, talking excessively, interrupting or intruding on others | Individuals rate the frequency of these symptoms in their lives. |
| PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 (PCL-5) | PTSD | Self-administered or clinician-guided questionnaire | 20 items assessing PTSD symptoms related to a stressful experience, including intrusive thoughts, nightmares, flashbacks, emotional distress, physical reactivity after exposure to traumatic reminders, avoidance of thoughts or reminders about the trauma, negative thoughts or feelings that began or worsened after the trauma, hyperarousal | Responses indicate how bothered the individual has been by each symptom over the past month. |
| Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): | Alcohol Use Disorder | Self Administered | A screening tool developed by the World Health Organization to identify persons with harmful alcohol consumption. | The responses are scored, and the total score of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) indicates the level of risk. A score of 8 or more indicates hazardous or harmful drinking behavior. The test can be administered quickly, usually taking less than 5 minutes to complete. |
How are Mental Health Screening Tests Conducted?
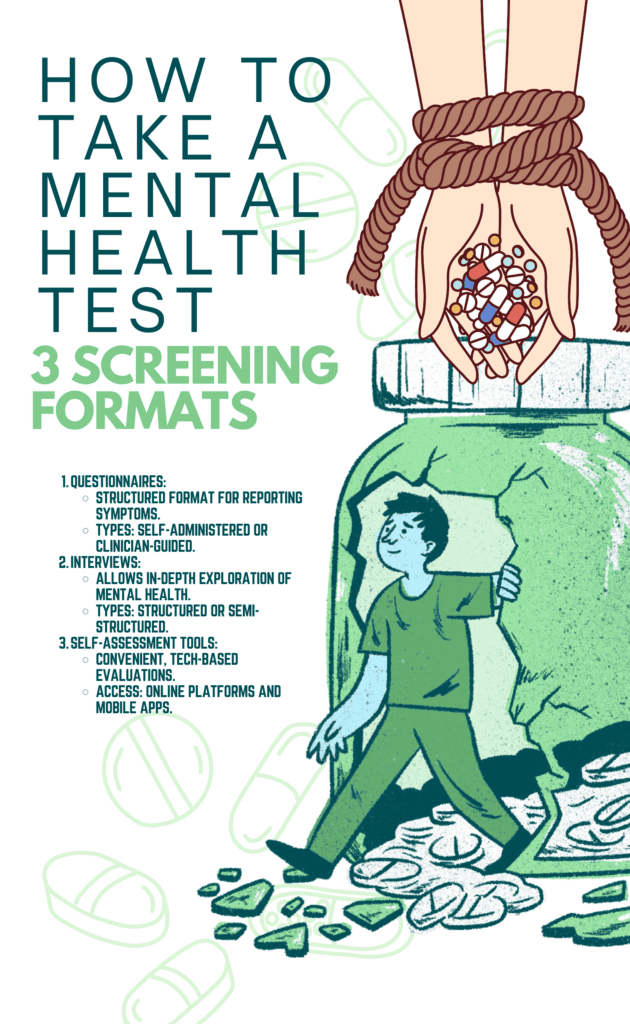
Mental health screening tests are conducted through questionnaires, clinician-led interviews, and self-assessment tools. These methods provide accurate insights into a person’s mental health and are accessible online or in clinical settings. Each approach plays a key role in guiding individuals toward the right care and support.
Here are some mental health screening test methods;
| Method | Format | Example | Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Questionnaires | Self-administered or Clinician-guided | “Over the past two weeks, how often have you been bothered by feeling down, depressed, or hopeless?” | Allows individuals to reflect on their symptoms and experiences, providing a structured format for reporting. |
| Interviews | Structured or Semi-structured | “Can you describe your current mood and how it affects your daily life?” | Facilitates a deeper exploration of an individual’s mental health status through direct conversation, enabling clinicians to assess symptoms and behaviors in depth. |
| Self-assessment Tools | Online Platforms and Mobile Applications | Mobile app tracking mood swings and patterns over time. | Offers a convenient and accessible way for individuals to evaluate their own mental health, with features like mood tracking, symptom logging, and providing feedback or resources. |
What is the Effectiveness of Mental Health Screening Tests?
The effectiveness of mental health screening tests lies in their ability to detect conditions early and guide individuals toward timely care. These tests are designed to be accurate, reliable, and widely applied in healthcare settings. Mental health screening tests play a vital role in early detection. Their limitations make professional follow-up important for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Here are some reasons why mental health tests are effective;
Accuracy in Diagnosing Mental Health Conditions
Mental health screening tests are built to identify early signs of mental health disorders with precision. They serve as a first step in recognizing potential problems. Mental health tests direct individuals toward further evaluation and care.
Sensitivity and Specificity Rates
These mental health screening tools are tested for their ability to measure accuracy. For instance, the PHQ-9 shows 88% sensitivity and 88% specificity for major depression, while the GAD-7 demonstrates 89% sensitivity and 82% specificity for anxiety. Similarly, the Mood Disorder Questionnaire (MDQ) reports a sensitivity of 73% and a specificity of 90% in community samples.
Limitations and Potential for Misdiagnosis
Behavioral health screening is not foolproof despite strong results. They sometimes produce false positives or negatives, mainly because they rely on how individuals describe their own symptoms.
Influence of Subjective Self-Reporting
Many mental health tests depend on self-assessment. Responses are influenced by perception, lack of awareness, or hesitation in sharing symptoms. This affects the accuracy of results.
Need for Follow-Up Clinical Assessment
Professionals must follow mental screenings with evaluation to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. Mental health experts interpret results, confirm conditions, and create tailored treatment plans that self-report tools alone cannot provide.
How Can Individuals Access Mental Health Screening Tests?
Individuals can access mental health screening tests through healthcare providers, online platforms, and community programs. Primary care doctors and specialists offer mental screenings with professional guidance and follow-up. Online self-assessment tools, available in free and paid versions, provide quick and private options. Community health organizations also host awareness and screening events, ensuring that people find support in ways that best fit their needs.
Here are some ways individuals can access mental health screenings;
- Through healthcare providers: Primary care physicians and mental health specialists are key resources for obtaining mental health screenings. They offer expertise and follow-up care.
- Online self-assessment tools: Online self-assessment tools offer a convenient and private way for individuals to evaluate their mental health. Tips for finding reliable tools include checking the credibility of the source, looking for reviews or endorsements from reputable mental health organizations, and considering privacy policies.
- Community health organizations: Community health organizations play a vital role in providing screenings as part of mental health awareness and screening programs. Individuals participating in these programs connect with local resources and support networks.
What is the Next Step After Completing a Mental Health Screening Test?
After a mental health screening, the next step is consulting a professional. The professional reviews results and confirms any diagnosis. A professional creates a personalized treatment plan that may include therapy, medication, or both. Regular follow-ups and adjustments ensure ongoing support and effective care.
Here are the steps that must be followed after completing a mental illness test;
Consultation with a Mental Health Professional
After a screening, an individual meets a mental health professional for evaluation and guidance. Different types of professionals provide support based on individual needs:
- Psychiatrists: Medical doctors who diagnose mental health conditions and manage treatment with medication.
- Psychologists: Experts in testing, evaluation, and therapy who offer behavioral and therapeutic interventions.
- LCSWs and LPCs: Licensed counselors and social workers who provide therapy, coping strategies, and emotional support.
Discussing Test Results and Implications
The consultation provides an opportunity to discuss the test results and their implication. This ensures that the individual fully understands their condition. The discussion allows individuals to ask questions. It also helps them express concerns and learn about the disorder identified by the screening.
Developing a Treatment Plan
Treatment plans are tailored to individual needs and circumstances. Treatment plans include:
- Individual Therapy: One-on-one sessions focusing on specific issues and personal growth.
- Group Therapy: Facilitated sessions with others experiencing similar issues, providing peer support.
- Medication: Psychiatrists prescribe medication to manage symptoms effectively.
- Lifestyle Changes: Include recommendations for exercise, diet, and sleep habits that support mental health.
Medication and Therapy
The mental health treatment involves medication, therapy, or a combination of both, depending on the nature and severity of the condition. The decision is made collaboratively, considering the individual’s preferences, lifestyle, and the specific mental health disorder.
Ongoing Monitoring and Support
Ongoing monitoring and support are integral to the treatment plan. Monitoring and Support provide the necessary adjustments and encouragement throughout the recovery process.
This includes:
- Regular Check-ins: Scheduled appointments to discuss progress, challenges, and any needed changes in treatment.
- Support Groups: Participation in groups for additional community support and shared experiences.
- Crisis Management Plans: Preparing for potential crises with strategies and contacts for immediate support.
Regular Follow-Ups and Adjustments to Treatment
Regular follow-ups with the mental health professional allow for adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. The follow-up ensures the most effective care and support.
These follow-ups are important for:
- Evaluating Medication Efficacy: Adjusting dosages or changing medications based on side effects and symptom management.
- Therapeutic Progress: Assessing the effectiveness of therapy approaches and making changes as necessary.
- Overall Well-being: Monitoring general health and well-being, addressing any new or ongoing issues.
This comprehensive approach to post-screening care ensures that individuals are supported throughout their journey to improved mental health, with adjustments made as needed to align with their evolving needs and circumstances.
Share This Post













